Introduction
In the contemporary landscape of digital transformation, effective data management has emerged as a cornerstone for organizations seeking to harness the full potential of cloud computing. This multifaceted discipline not only encompasses the storage and organization of vast quantities of data but also emphasizes the critical importance of security, governance, and integration within cloud environments.
As enterprises pivot from traditional on-premises infrastructure to more dynamic cloud solutions, they unlock significant advantages such as enhanced scalability, cost efficiency, and improved collaboration. However, this shift is not without its challenges, as organizations must navigate complex security concerns and compliance regulations.
This article delves into the essential aspects of cloud data management, comparing it to traditional methods, exploring key benefits, and outlining best practices to ensure robust and effective data handling in the cloud.
Defining Data Management in Cloud Computing
Data management in cloud computing involves the systematic procedures and technologies that businesses use to store, arrange, and oversee information within online environments. This multifaceted discipline includes essential functions such as:
- Information storage
- Integration
- Quality assurance
- Governance
- Security
In contrast to conventional information handling, data management in cloud computing enhances flexibility, scalability, and accessibility by utilizing cloud resources instead of relying on on-premises infrastructure.
This method allows entities to effectively manage large volumes of information through data management in cloud computing while ensuring its accessibility for analysis and informed decision-making. Consequently, organizations can coordinate their strategies for data management in cloud computing with business goals, promoting innovation and enhancing competitive advantage. Recent trends indicate a growing acceptance of online solutions, with over 80% of the market concentrated among the top five IaaS providers, such as Amazon and Microsoft.
Notably, Alibaba Cloud secured a 4% market share in 2023, illustrating the competitive landscape. Moreover, the 2022 Thales Data Report disclosed that 83% of participants indicated at least half of their sensitive information is unprotected while stored in remote servers, highlighting the urgent necessity for strong data management in cloud computing practices to address security issues. Furthermore, as emphasized by The Motley Fool, Palantir reached $1.91 billion in revenue for fiscal year 2022, demonstrating a successful model in the sector that highlights the significance of data management in cloud computing in fostering business success.
Key Benefits of Cloud Data Management
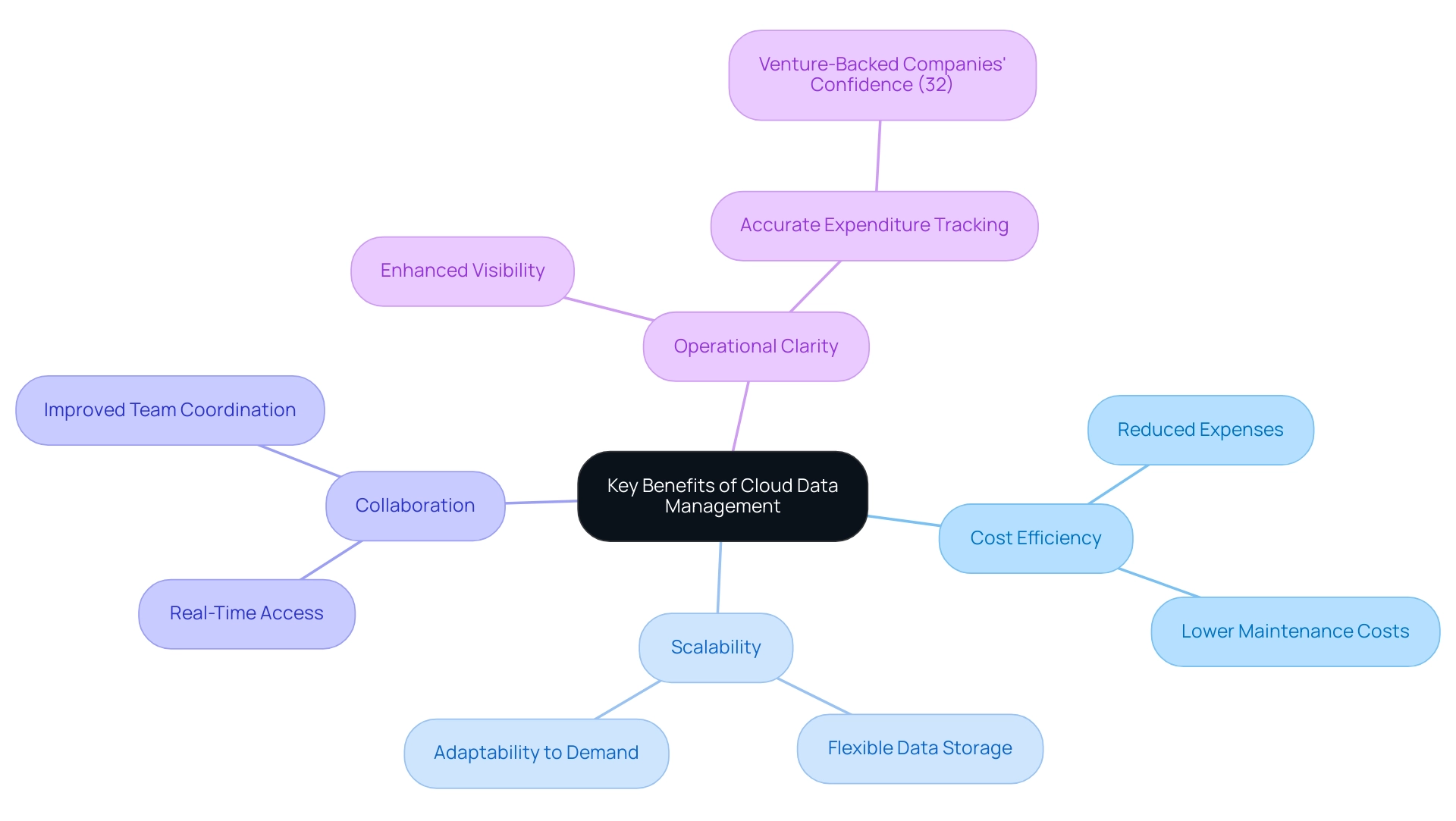
Organizations that adopt comprehensive data management in cloud computing solutions unlock a range of pivotal benefits, primarily centered on cost efficiency, enhanced scalability, and strengthened collaboration. By utilizing online resources, enterprises can significantly decrease the expenses tied to maintaining physical servers and infrastructure. The rapid expansion of Google Cloud Services, which experienced a 63.7% rise in its Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offerings, exemplifies the changing landscape toward more cost-effective solutions, particularly as Google holds an 11% market share compared to Alibaba's 4%.
Furthermore, online platforms facilitate the seamless scaling of data storage and processing capabilities, allowing businesses to swiftly adapt to fluctuating demands. This flexibility becomes crucial in light of recent findings, which indicate that in 2024, only 32% of venture-backed companies exhibit confidence in accurately attributing their expenditures—a stark contrast to prior years when public companies struggled with visibility. As observed, 'In 2024, venture-backed companies report having the least confidence in attributing expenditure on online services (32%).'
This trend highlights the importance of strong data management in cloud computing to enhance operational clarity and efficiency. Additionally, the case study titled "Visibility Challenges for Venture-Backed Companies" highlights that only 32% of these companies can accurately track their expenditures related to online services, marking a significant shift from previous years. Effective data management in cloud computing promotes better collaboration by allowing teams to access and share essential information from almost any location, thereby improving real-time decision-making and encouraging innovation.
This accessibility is particularly advantageous for remote and distributed teams, streamlining their ability to collaborate on data-driven initiatives and projects. Ultimately, the incorporation of efficient data management in cloud computing not only addresses current operational issues but also allows entities to thrive in an increasingly competitive environment.
Comparing Traditional and Cloud Data Management
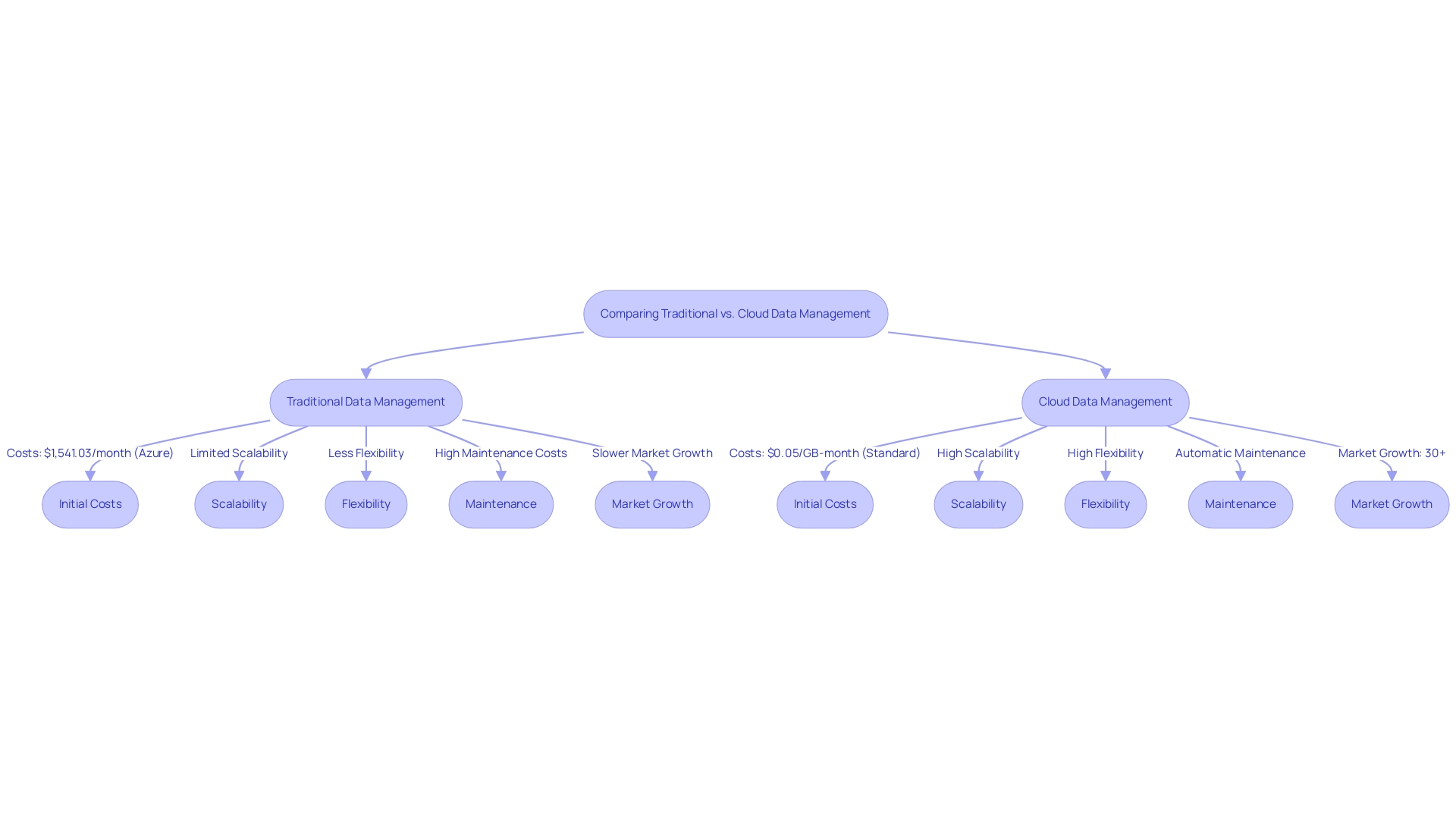
Conventional information handling systems generally necessitate considerable expenditures in on-site equipment, software licenses, and continuous upkeep, leading to significant initial expenses and limited scalability. For instance, an Azure Cloud Services instance with 112 GB RAM and 800GB temporary storage incurs a monthly cost of $1,541.03, highlighting the financial commitment associated with maintaining such setups. In contrast, data management in cloud computing solutions enable entities to bypass extensive on-site infrastructure and embrace a pay-per-use model for resources utilized.
Pricing for Amazon EBS snapshots illustrates this flexibility, with standard storage priced at $0.05 per GB per month and archive storage at $0.0125 per GB per month, simplifying budget management for businesses. Additionally, solutions provide automatic updates and maintenance, greatly lessening the operational load on IT staff. The agility of data management in cloud computing allows organizations to quickly react to changing information needs, such as increasing storage capabilities or incorporating new applications, a process often burdensome in conventional settings.
Notably, the IaaS market is expected to grow over 30%, with Google Cloud's IaaS offering growing at 63%, indicating a strong market preference for these flexible solutions. According to Cody Slingerland,
The U.S. and Western Europe still dominate computing services,
further emphasizing this trend. A case study on information integration and supervision reveals that while manual processes in information centers can be labor-intensive, online storage provides advanced automated integration tools that enhance user-friendliness.
This case study shows that organizations utilizing online solutions reported a 40% decrease in information integration time compared to conventional methods. Overall, data management in cloud computing emerges as a more flexible and economical approach for businesses maneuvering through the intricacies of information handling, though conventional centers still provide greater control over the information oversight process.
Challenges and Risks in Cloud Data Management
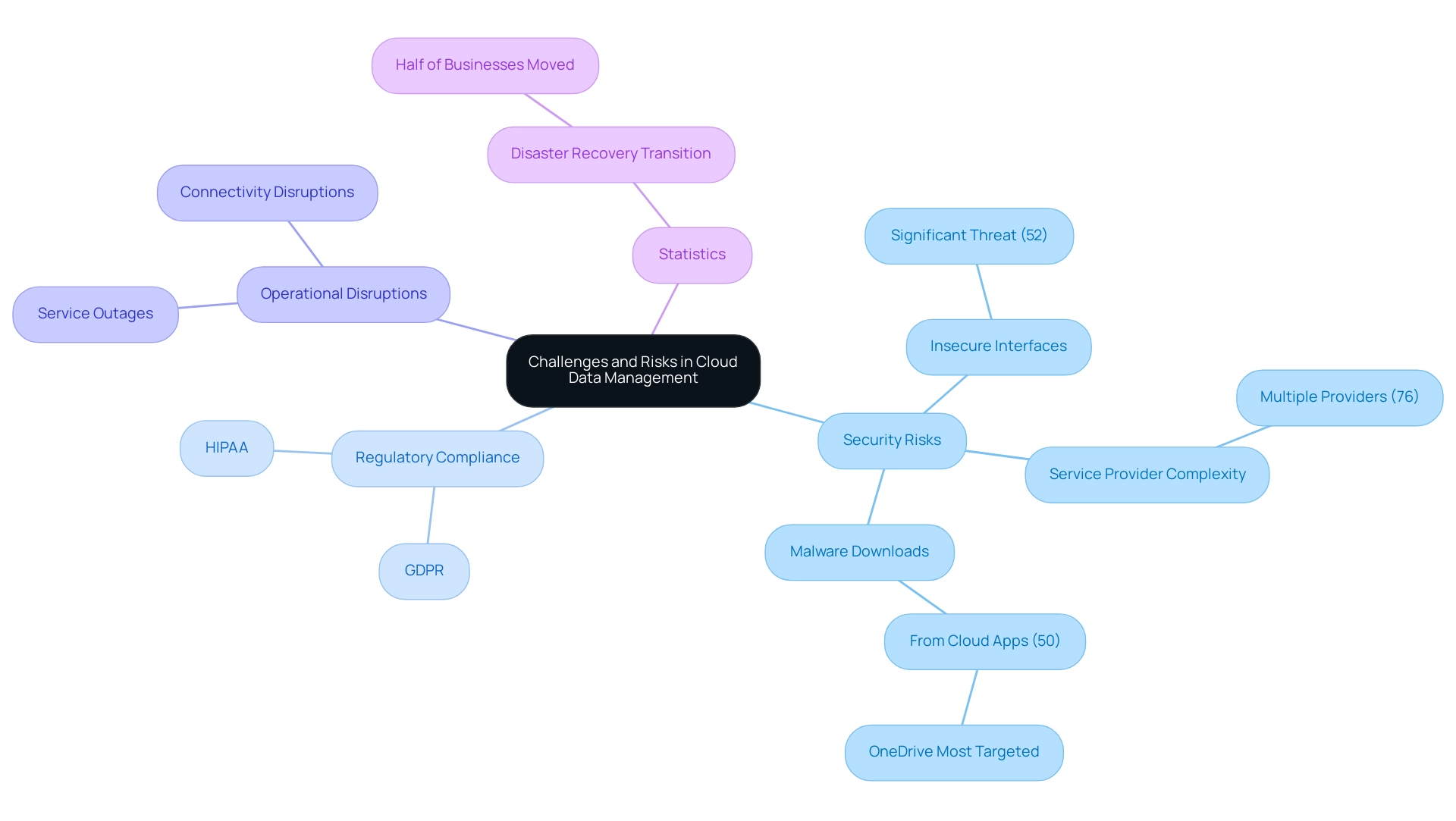
As companies increasingly depend on data management in cloud computing, it is crucial to recognize the complex challenges and risks that accompany this transition. Significantly, 76% of entities employ various service providers, which can worsen the complexities of security in the digital environment. Moreover, recent findings reveal that 52% of organizations consider insecure interfaces in public online environments to be a significant security threat.
Such vulnerabilities can lead to data breaches, particularly as sensitive information stored online remains susceptible to attacks if proper security protocols are not enforced. In 2023, over 50% of HTTP and HTTPS malware downloads were traced back to cloud-based SaaS applications, with OneDrive identified as the most frequently targeted app. This emphasizes the urgent need for robust security measures designed for online infrastructures.
As Cody Slingerland observes, "Together, these two areas represent 82% of the world’s computing," highlighting the importance of tackling these challenges in a fiercely competitive environment.
Adherence to data protection regulations, like GDPR and HIPAA, further complicates data management in cloud computing. Organizations must navigate intricate regulatory landscapes, ensuring their strategies align with legal requirements to avoid potential penalties. In fact, half of surveyed businesses transitioned to remote services primarily for disaster recovery, illustrating the necessity of having a secure and compliant strategy that also addresses operational resilience.
Furthermore, service outages or connectivity disruptions can lead to significant downtime, jeopardizing access to critical business information and disrupting operations. By thoroughly comprehending and tackling these obstacles, entities can create effective risk handling strategies that safeguard their information assets in the digital space, ensuring both security and adherence in an increasingly intricate environment.
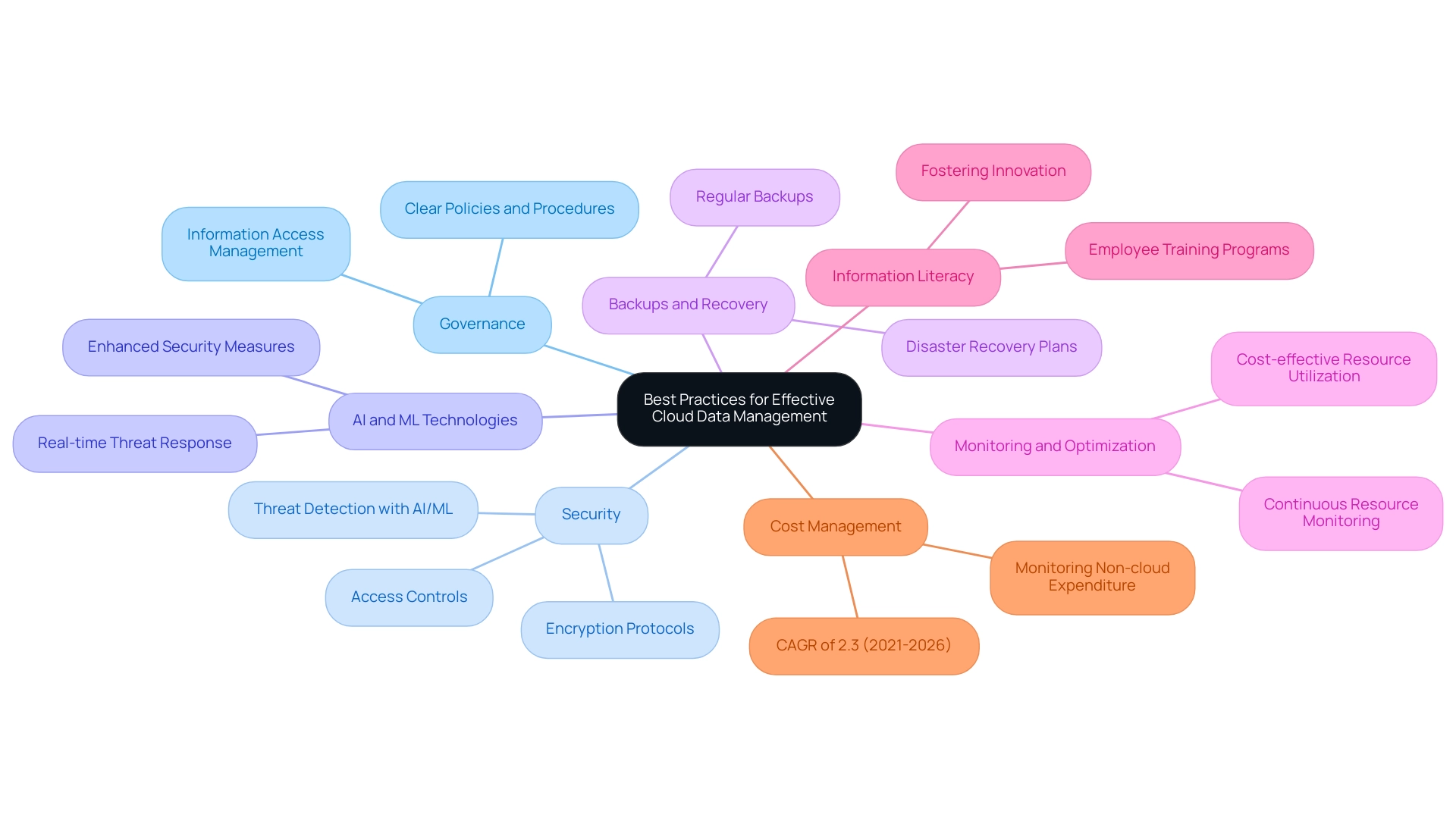
Best Practices for Effective Cloud Data Management
To achieve effective data management in cloud computing, organizations must implement a series of best practices that prioritize governance and security. Establishing clear policies and procedures regarding information access, usage, and security is paramount. Robust information encryption protocols and stringent access controls are essential to safeguarding sensitive details against threats.
Moreover, leveraging AI and ML technologies can enhance security by identifying and responding to threats in real-time, providing an additional layer of protection. Regular backups and comprehensive disaster recovery plans are critical to mitigating the potential impacts of loss or service interruptions. Continuous monitoring and optimization of online resources ensure that organizations leverage their investments efficiently and cost-effectively.
Promoting a culture of information literacy within the workforce empowers employees to utilize information effectively, enhancing decision-making and fostering innovation. Furthermore, it is significant that expenditure on non-cloud infrastructure is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 2.3% from 2021 to 2026, emphasizing the evolving environment toward digital solutions. By following these best practices, organizations can significantly enhance the benefits of data management in cloud computing while simultaneously reducing related risks.
As Cody Slingerland observes, the need for effective online computing strategies is evident, with regions making up 82% of the world’s computing. Furthermore, the growth of Google Cloud's IaaS offering by 63.7% underscores the urgency for enterprises to adopt best practices in data management in cloud computing as they navigate an increasingly complex digital landscape.
Conclusion
In the current era of digital transformation, effective cloud data management stands out as a critical component for organizations striving to maximize the benefits of cloud computing. The systematic processes involved in cloud data management not only facilitate the storage and organization of data but also enhance security, governance, and integration, which are essential for informed decision-making and operational efficiency. The advantages of adopting cloud solutions, such as cost efficiency, scalability, and improved collaboration, position organizations to meet evolving market demands and drive innovation.
However, transitioning to cloud data management is not without its challenges. Organizations must navigate security risks, compliance regulations, and the complexities of managing multiple cloud environments. As highlighted, the prevalence of vulnerabilities within cloud infrastructures necessitates robust security measures and a comprehensive understanding of the regulatory landscape. Developing effective risk management strategies is crucial for safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring compliance, thereby protecting organizational assets in increasingly competitive environments.
To harness the full potential of cloud data management, organizations are encouraged to implement best practices that prioritize data governance and security. By establishing clear policies, leveraging advanced technologies, and promoting a culture of data literacy, businesses can not only mitigate risks but also enhance their operational capabilities. As the landscape continues to evolve, embracing these strategies will empower organizations to thrive in the digital age, ultimately reinforcing the significance of effective cloud data management as a cornerstone of modern business success.




