Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cloud computing, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has established itself as a cornerstone for businesses seeking agility and efficiency. As organizations increasingly turn to cloud solutions to optimize operations and drive innovation, AWS offers a comprehensive suite of services that cater to diverse industry needs.
From scalable computing power and secure storage options to advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities, AWS empowers enterprises to harness the full potential of their data while minimizing infrastructure costs.
However, navigating the complexities of AWS, including its pricing models and potential vendor lock-in, requires careful consideration. This article delves into the multifaceted world of AWS, examining its core functionalities, advantages and challenges, and transformative applications across various sectors, ultimately providing insights into its pivotal role in shaping the future of cloud computing.
Defining Amazon Web Services (AWS): An Overview
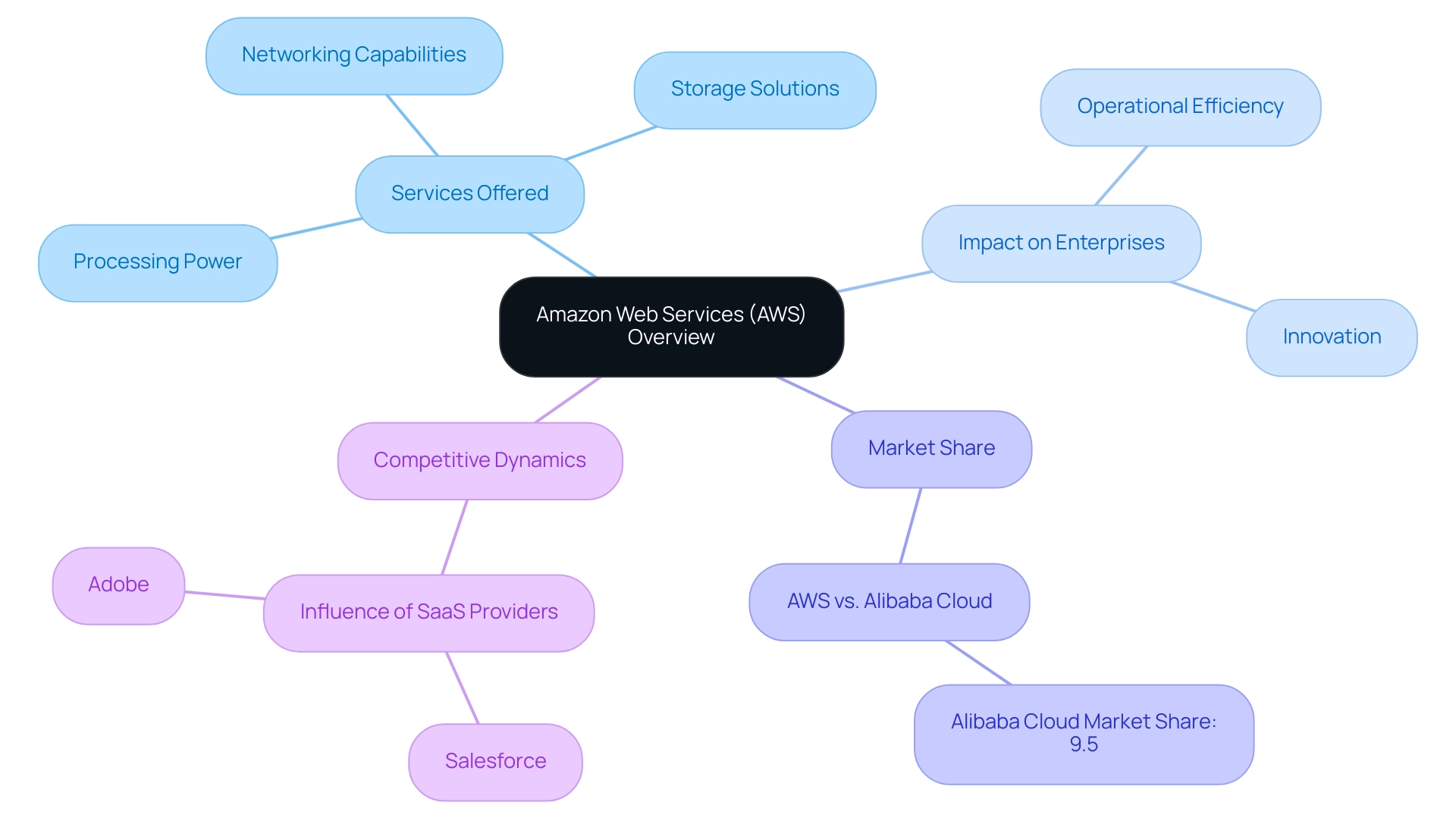
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is an all-encompassing platform offered by Amazon, which is AWS Cloud, celebrated for its wide range of online solutions. These services include processing power, storage solutions, and networking capabilities, empowering organizations to operate with remarkable agility and efficiency. The solution that is AWS Cloud offers scalable resources on-demand, eliminating the need for substantial upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure, which is a critical consideration for enterprises aiming to optimize their operational costs.
As a frontrunner in the computing landscape, the service that is AWS Cloud has fundamentally transformed the deployment and management of applications across various industries. This transformation not only enhances innovation but also elevates operational efficiency, enabling organizations to harness actionable insights from their data. The strategic adoption of what is AWS Cloud is evidenced by its influence on enterprises, with significant contributions to driving informed decision-making and fostering innovation in a rapidly evolving technological environment.
Notably, AWS competes in a market where Alibaba Cloud holds a 9.5% market share, highlighting its competitive position. A case study titled 'Digital Transformation through AWS' illustrates how AWS provides access to advanced technologies that enable enterprises to modernize applications and improve scalability, empowering businesses to derive actionable insights from data. Furthermore, industry leaders such as Adobe highlight that 'SaaS providers like Salesforce and Adobe possess substantial market influence,' emphasizing the competitive dynamics at play in the services sector.
How AWS Works: Core Services and Functionality
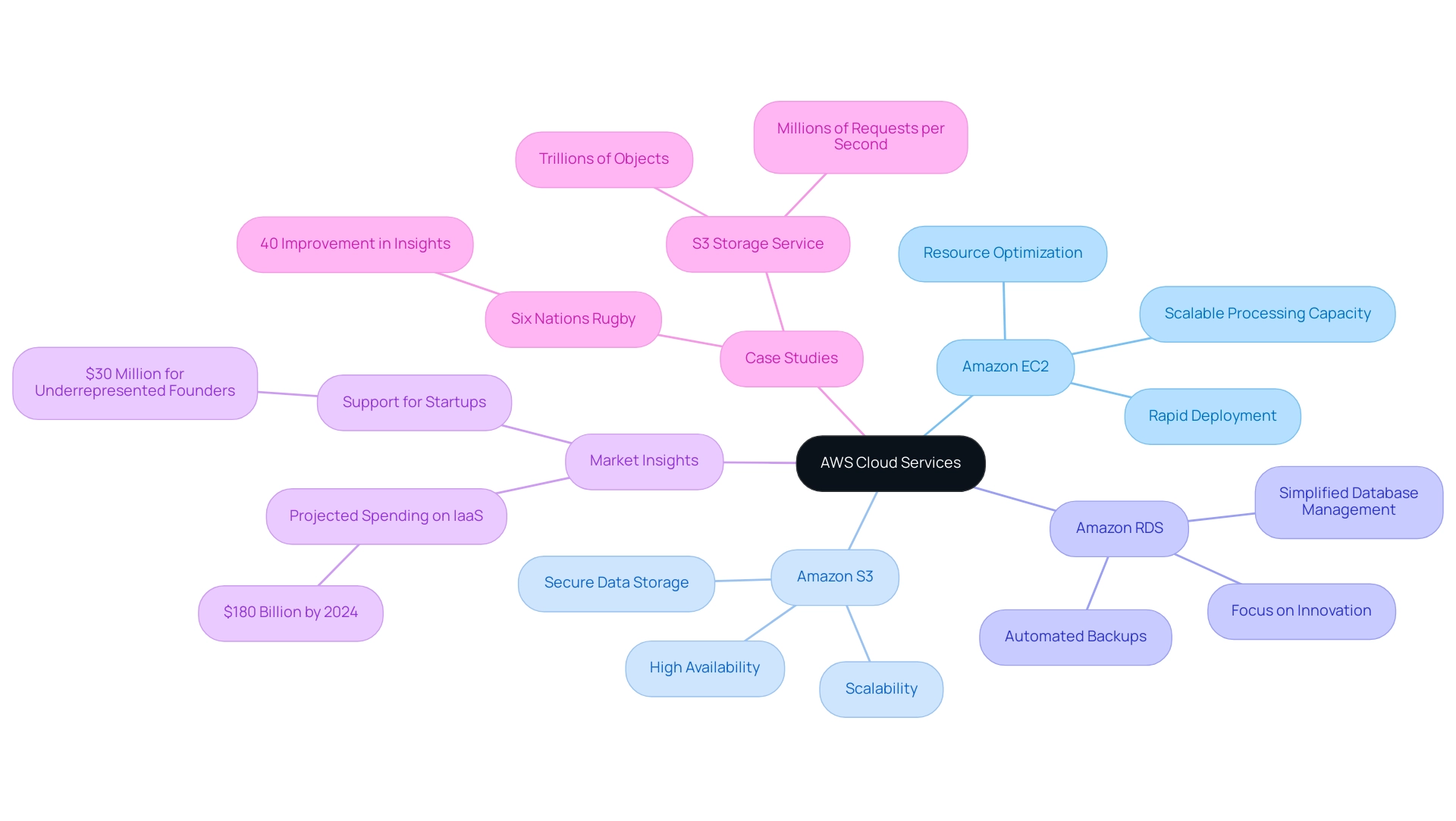
The pricing structure of AWS Cloud is pay-as-you-go, enabling businesses to adjust their usage dynamically based on demand. This approach is particularly advantageous for Chief Technology Officers seeking to optimize resource allocation while minimizing costs. Among AWS's core offerings, Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) is AWS cloud that provides scalable processing capacity, enabling rapid deployment and adjustment of resources.
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) stands out for its secure and resilient data storage capabilities, capable of handling trillions of objects and serving millions of requests per second. As Lionel Sujay Vailshery, a research expert focusing on computing, states, "Accordingly, AWS provides a wide range of internet-based products, including databases, analytics, management tools, security, IoT, enterprise applications, and developer tools." Furthermore, Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) is AWS Cloud that simplifies database management, enabling businesses to focus on innovation rather than infrastructure complexities.
A complete toolkit for application development and deployment is AWS Cloud, which expands its capabilities into machine learning, analytics, and Internet of Things (IoT) along with these essential offerings. Significantly, the recent use of AWS computing resources by Six Nations Rugby demonstrates how data gathering and analysis can be improved, leading to an impressive 40% enhancement in the precision and promptness of insights. The scalability and reliability of Amazon S3 are further illustrated by its ability to store trillions of objects and serve millions of requests per second, making it a preferred choice for businesses needing robust storage solutions.
The core of this technological shift is AWS Cloud, as it continues to release new features and updates—especially regarding Amazon EC2 and S3—enabling businesses to maintain agility while ensuring robust control over their IT environments. With public infrastructure as a solution (IaaS) end-user expenditure anticipated to hit $180 billion by 2024, the shift to AWS signifies not only a strategic investment but also a route toward operational excellence.
Pros and Cons of Using AWS: Weighing the Benefits and Drawbacks
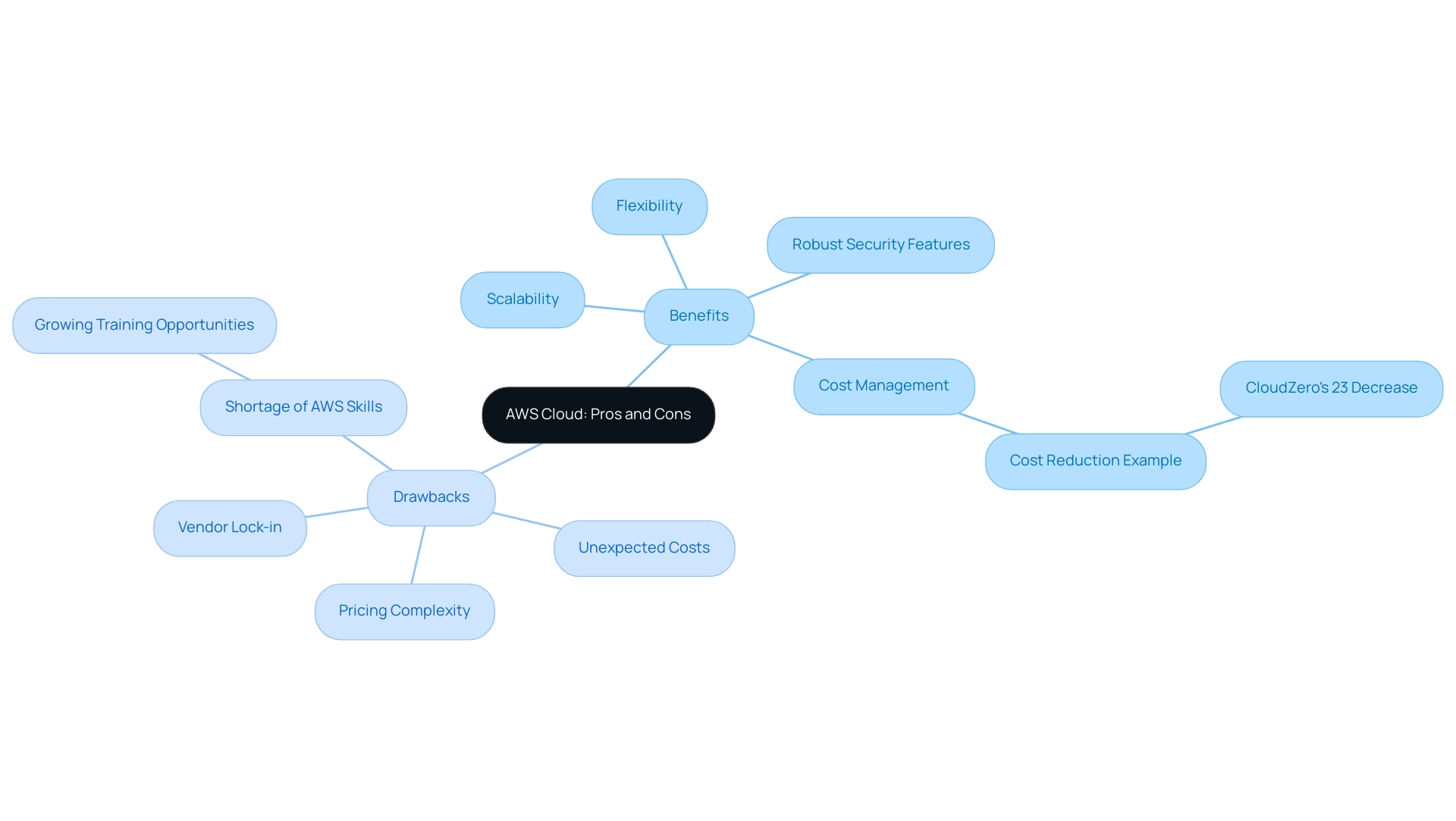
One of the pivotal benefits for modern businesses is AWS Cloud, particularly its remarkable scalability and flexibility. Organizations can swiftly adjust their resource allocation in response to fluctuating workloads, a crucial advantage in today’s dynamic market landscape. Furthermore, what is AWS Cloud is a comprehensive suite of services coupled with robust security features and compliance certifications, making it an ideal choice for industries subject to stringent regulations.
A notable example of cost management is illustrated by CloudZero, which integrated AWS and saw their expenditure decrease by 23%. However, the platform is not without its challenges. The intricacies of its pricing models can result in unexpected costs, a concern echoed by many businesses navigating AWS’s expansive offerings.
In fact, recent statistics indicate that the complexity of AWS pricing is a significant hurdle for organizations, with many encountering costs that exceed initial estimates. Additionally, the potential for vendor lock-in necessitates a thorough evaluation of long-term strategies for online services. The increasing need for AWS skills, fueled by the swift transition of businesses to virtual services, highlights that the current landscape for organizations aiming to optimize their AWS investments is AWS Cloud, as there is a significant shortage of qualified professionals.
As noted in a case study titled 'Demand for AWS Skills,' this shortage presents growing opportunities for training and career development in AWS-related fields. As Cody Slingerland states,
Combined, these two regions account for 82% of the world’s computing,
underscoring the dominance of AWS in the market. Ultimately, while the platform that is AWS Cloud presents unparalleled opportunities for scalability and is a modern data protection strategy for businesses, organizations must carefully navigate its complexities to fully leverage its capabilities.
Applications of AWS: Transforming Industries with Cloud Solutions
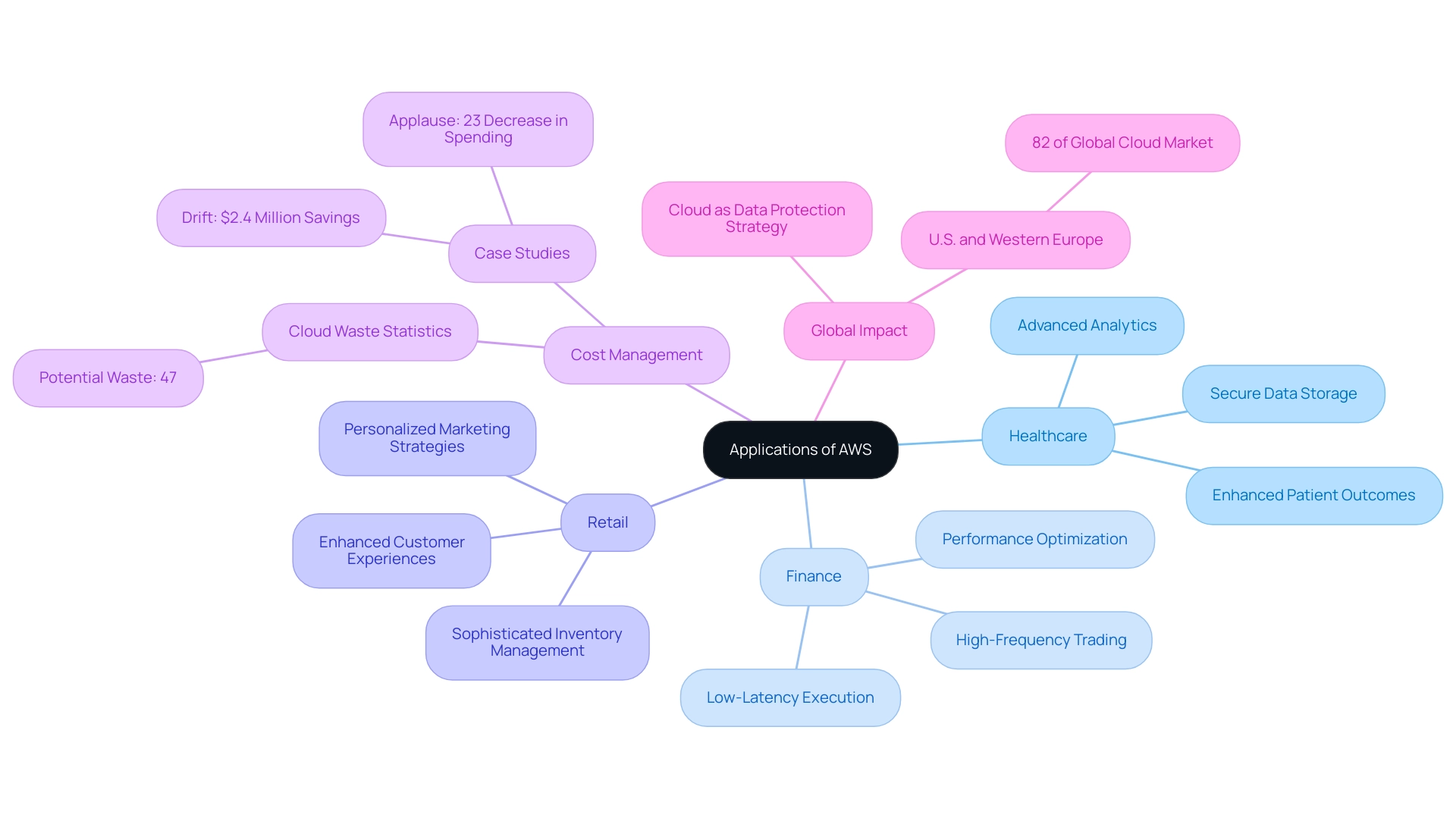
AWS has emerged as a pivotal force in reshaping industries such as healthcare, finance, and retail. In the healthcare sector, organizations harness AWS for secure data storage and advanced analytics, which facilitate data-driven insights that significantly enhance patient outcomes. Recent statistics indicate that the applications of AWS in healthcare are projected to grow substantially by 2024, underscoring its critical role in modern healthcare infrastructure.
Furthermore, with waste from online services potentially reaching as high as 47% of a budget, efficient management of AWS resources is crucial for organizations seeking to optimize their spending. In finance, companies are increasingly utilizing AWS for high-frequency trading applications, capitalizing on the platform's low-latency capabilities to execute trades with unparalleled speed and efficiency. This capability is essential for firms aiming to optimize their performance in a highly competitive market.
For instance:
- Drift successfully reduced its annual expenses for online services by $2.4 million.
- Applause achieved a 23% decrease in spending through effective cost management strategies.
Meanwhile, retailers leverage AWS to elevate customer experiences through personalized marketing strategies and sophisticated inventory management solutions. These varied applications demonstrate that AWS Cloud is a powerful tool for promoting innovation and enhancing operational efficiencies across multiple sectors, reinforcing its status as a leader in online services.
As mentioned by industry expert Cody Slingerland, 'Together, these two regions represent 82% of the world’s cloud services,' emphasizing the substantial impact of AWS in the U.S. and Western Europe, which lead the global cloud services landscape.
The Future of AWS: Innovations and Trends in Cloud Computing
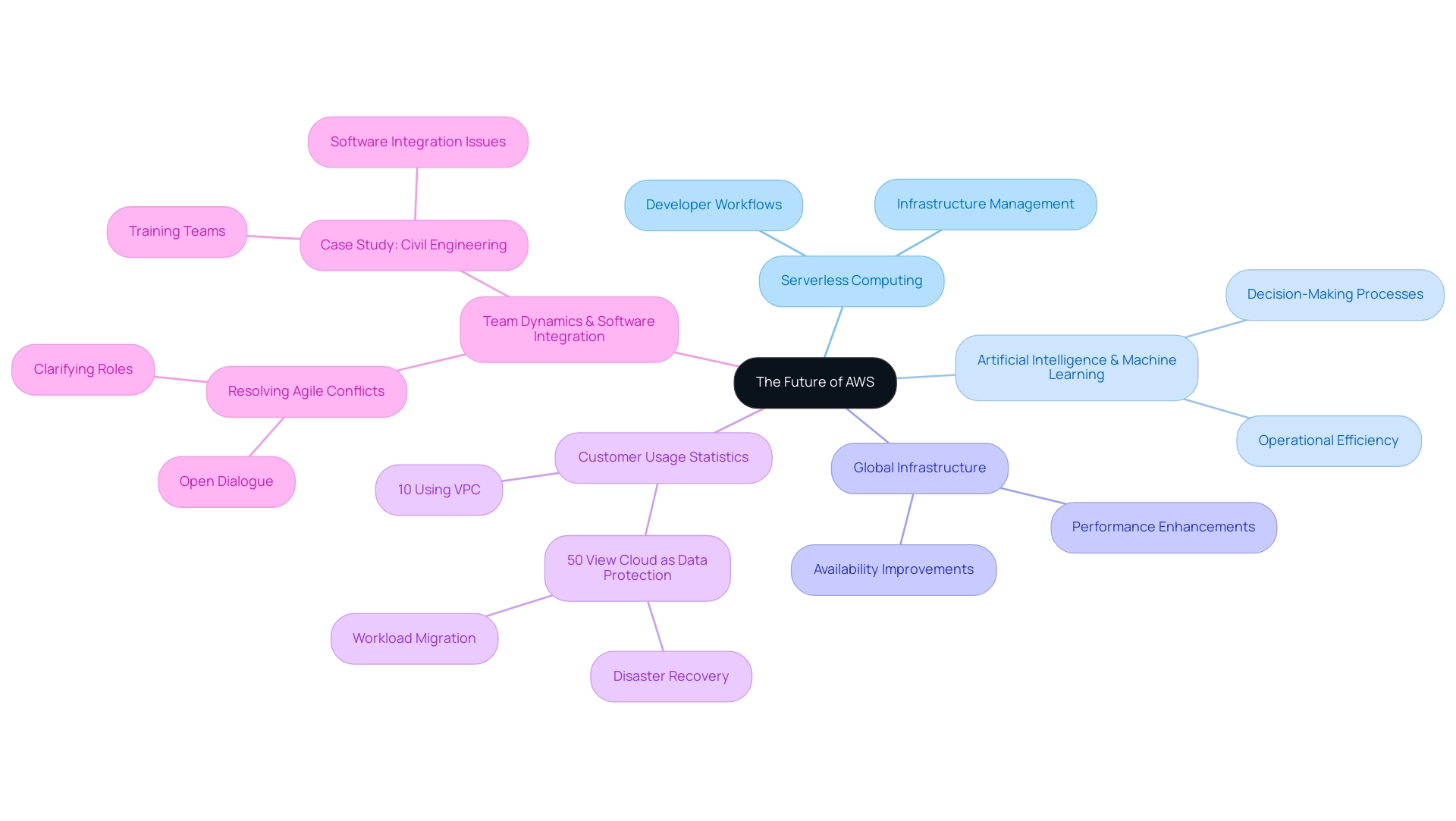
The future landscape of AWS is characterized by relentless innovation and responsiveness to emerging technological trends. Notably, the ascendancy of serverless computing is transforming developer workflows, enabling them to concentrate on code development without the burdens of infrastructure management. This shift is further complemented by the growing significance of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities integrated within AWS offerings, enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making processes.
Additionally, AWS is dedicated to enhancing its global infrastructure, thereby improving availability and performance across diverse geographical locations. Currently, 10 percent of customers run all of their functions with their own Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), highlighting the importance of secure and scalable networking solutions. With a notable 50% of surveyed businesses identifying computing services as integral to their data protection strategies—often utilizing it for disaster recovery and workload migration—AWS recognizes the necessity for interoperability amidst the rise of hybrid environments.
As Mike Stemle, Principal Architect at Arc XP, notes, 'Teams adopting Lambda still need to make informed decisions based on their security, performance, and functional requirements, which won’t be one-size-fits-all.' This approach ensures that organizations can seamlessly integrate their operations across various platforms. Furthermore, as companies adapt to these transformative trends, addressing conflicts in Agile teams by fostering open dialogue and clarifying roles will be crucial.
The case study on tackling software integration issues in civil engineering exemplifies the need for evaluating compatibility and training teams to ensure smooth project execution. Remaining informed about AWS innovations will be essential for leveraging cloud services as a competitive advantage.
Conclusion
The exploration of Amazon Web Services (AWS) reveals its foundational role in the cloud computing landscape, offering an extensive array of services that enhance operational agility and efficiency across various industries. Through its scalable computing power, secure storage solutions, and advanced analytical capabilities, AWS empowers businesses to optimize their operations while minimizing costs. The pay-as-you-go pricing model further facilitates dynamic resource allocation, making it an appealing choice for organizations navigating the complexities of modern technology.
While AWS presents remarkable advantages, such as scalability and a comprehensive suite of services, it also poses challenges, particularly regarding pricing complexities and potential vendor lock-in. Organizations must remain vigilant and informed to mitigate unexpected costs and ensure that their cloud strategies align with long-term goals. The growing demand for AWS expertise highlights the need for ongoing training and development, positioning AWS not just as a cloud service provider but as a catalyst for innovation and operational excellence.
As AWS continues to transform industries—ranging from healthcare to finance and retail—it is evident that its influence will only expand in the future. By embracing innovations like serverless computing and integrating artificial intelligence, AWS is poised to redefine how organizations approach their cloud strategies. In this rapidly evolving technological landscape, staying abreast of AWS's advancements will be crucial for businesses seeking to leverage its capabilities for sustained competitive advantage. The journey with AWS is not merely about adopting cloud services; it is about embracing a transformative approach that can redefine operational paradigms and drive meaningful outcomes in an increasingly data-driven world.




