Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital technology, cloud security has emerged as a paramount concern for organizations striving to protect their data and maintain operational integrity. As businesses increasingly migrate to cloud environments, understanding the foundational principles of cloud security becomes essential.
Central to this understanding is the CIA triad—confidentiality, integrity, and availability—which serves as the bedrock of effective security frameworks. This article delves into vital strategies and best practices for implementing robust cloud security measures, emphasizing the importance of:
- Data protection
- Identity and access management
- The shared responsibility model
Through a comprehensive exploration of these topics, organizations can equip themselves with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of cloud security and safeguard their digital assets against an ever-growing array of threats.
Foundational Principles of Cloud Security
The principles of cloud security are essential for organizations aiming to safeguard their cloud environments. At the core of these principles is the CIA triad, which encompasses data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. This triad forms the cornerstone of any effective protective framework, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure and accessible only to authorized users.
Furthermore, the principle of least privilege is critical, advocating that users and applications should be granted only the minimal access required to perform their functions, significantly mitigating potential risks. Openness in protective practices promotes trust, as it entails clear communication about protective measures and policies, while accountability guarantees that all stakeholders comprehend and accept their protective responsibilities within the infrastructure.
Recent statistics emphasize the urgency of these principles, with the global online protection software market anticipated to expand from $29.5 billion in 2020 to around $37 billion by 2026, highlighting the necessity for organizations to invest in strong protective measures. A significant instance of effective protective measures is demonstrated in a case study titled 'Encrypting Information on the Cloud,' which highlights that encrypting information is a fundamental protective practice that safeguards sensitive content from unauthorized access by transforming it into a coded format. Efficient encryption techniques greatly minimize the threat of data breaches and compliance infractions, improving overall data protection and privacy in online environments.
Furthermore, based on the 2024 Thales Data Threat Report, only 46% of participants indicated that more than 40% of staff at the company are utilizing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for cloud-based applications, highlighting the significance of adopting such protective measures. Successful application of the principles of cloud security is crucial for entities aiming to create a strong protective stance in the digital realm, especially in light of increasing dangers, as demonstrated by the recent breach of 1.5 billion records from the Real Estate Wealth Network in December 2023.
Best Practices for Implementing Cloud Security Strategies
Successfully executing online protection strategies requires organizations to prioritize several essential best practices, including the principles of cloud security. First and foremost, conducting regular security assessments and audits is vital for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring compliance with the principles of cloud security and industry security standards. With over 50% of sensitive information assets stored online accessed by only five to ten applications, understanding the landscape of potential risks is vital.
Furthermore, utilizing encryption for information both in transit and at rest is essential for safeguarding sensitive content from unauthorized access, as outlined by the principles of cloud security. The effectiveness of encryption in online data protection cannot be overstated, as it serves as a critical barrier against potential breaches and is essential to the principles of cloud security within any robust protection strategy.
Organizations should also establish comprehensive incident response plans that incorporate the principles of cloud security to address breaches swiftly and efficiently. This is especially relevant considering that the typical expense of a breach in a hybrid computing environment is around 3.61 million dollars, emphasizing the financial consequences of insufficient protective measures. Furthermore, ongoing employee education on the principles of cloud security and phishing prevention is essential, as human error remains a major risk factor in data incidents.
To further improve their protective stance in line with the principles of cloud security, organizations should utilize advanced protective tools such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and multi-factor authentication. A recent survey showed that 57% of companies with small IT protection teams are prioritizing online solutions, indicating a clear trend towards cloud-first strategies. Significantly, 76% of businesses utilize a minimum of two service providers, which adds to the complexity of managing data protection.
As Grace Lau, Director of Growth Content, observes, 'According to Gartner, by 2024, 60% of infrastructure and operations leaders will experience public cost overruns that adversely impact their available budgets.' This emphasizes the necessity for efficient execution of online protection methods aligned with the principles of cloud security to reduce risks and enhance operational effectiveness. By integrating the principles of cloud security as best practices, organizations can not only protect their data but also position themselves strategically for future digital transformations.
Furthermore, a survey revealed that 72% of IT security leaders perceive the online infrastructure as a top priority for digital transformation, emphasizing the essential nature of implementing security measures for it.
Data Protection: Safeguarding Information in the Cloud
Data protection in the cloud encompasses a wide array of strategies designed to secure information against unauthorized access, loss, or corruption, following the principles of cloud security. A crucial element of these strategies is the implementation of robust encryption protocols, which protect information both at rest and in transit. This ensures that even if information is intercepted during transmission, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
Furthermore, regular backups and the utilization of secure storage solutions are imperative for effective recovery in the event of a breach or loss. Entities should create information classification policies to recognize and prioritize sensitive material, applying enhanced controls to high-risk information accordingly.
The need for these protective measures is highlighted by alarming statistics; for instance, crypto mining was detected in two-thirds of cloud compromises in 2023. The recent 2023 Toyota Hack serves as a stark reminder that even well-established entities are vulnerable to simple misconfiguration errors, with sensitive information exposed for over eight years. Moreover, compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA is integral in shaping comprehensive protection strategies that align with the principles of cloud security, as organizations must adhere to legal requirements related to handling and privacy.
Significantly, OneDrive is mentioned as the application where malware downloads are most often identified, highlighting the persistent challenges related to safety in online environments. As expenditure on online protection is anticipated to rise from $4 billion in 2021 to over $6 billion in 2023, with service providers projected to represent more than 40% of overall protection spending, the focus on effective information safeguarding strategies grows ever more vital. This increasing expenditure emphasizes the need for entities to invest in advanced data protection strategies, including the adoption of new encryption protocols, especially as expert insights suggest that these advancements are crucial for securing data in light of the principles of cloud security and emerging threats in 2024.
Tackling the safety issues highlighted in the case study named 'Cloud Security Concerns' is crucial for successful adoption of online services, as many businesses still perceive computing safety as a major obstacle to migration.
Identity and Access Management: Securing User Access
Identity and Access Management (IAM) serves as a fundamental element of online protection, vital for ensuring user access in alignment with the principles of cloud security across various virtual environments. With 68% of entities recognizing account takeovers as a major threat, the necessity for strong IAM practices cannot be emphasized enough. Phishing accounts for over 25% of online protection attacks, as observed by Sentinel One, emphasizing the range of dangers organizations encounter.
Implementing role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that users are granted access strictly to the resources necessary for their specific roles, thus minimizing potential vulnerabilities. Moreover, the principles of cloud security emphasize that multi-factor authentication (MFA) is essential in strengthening protection; it requires users to give additional confirmation beyond simply inputting a password, establishing an extra hurdle against unauthorized access.
The intricacy of online data protection is additionally highlighted by the fact that 76% of enterprises utilize at least two service providers, which underscores the importance of the principles of cloud security and effective IAM practices. Regularly reviewing and updating access permissions is vital, especially as personnel and job functions evolve. This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data.
The concerning December 2023 event involving the Real Estate Wealth Network, which led to the exposure of 1.5 billion records, highlights the necessity for entities to implement rigorous online protection measures.
To further improve safety, entities should consider automated IAM solutions that simplify user provisioning and de-provisioning processes. Such systems ensure that access rights are promptly revoked when no longer needed, thereby strengthening the overall protection posture. As organizations progressively invest in Security Awareness Training (SAT) to educate employees on cyber safety, especially concerning password and credential verification, it becomes more essential than ever to integrate the principles of cloud security in defending against the evolving landscape of online threats.
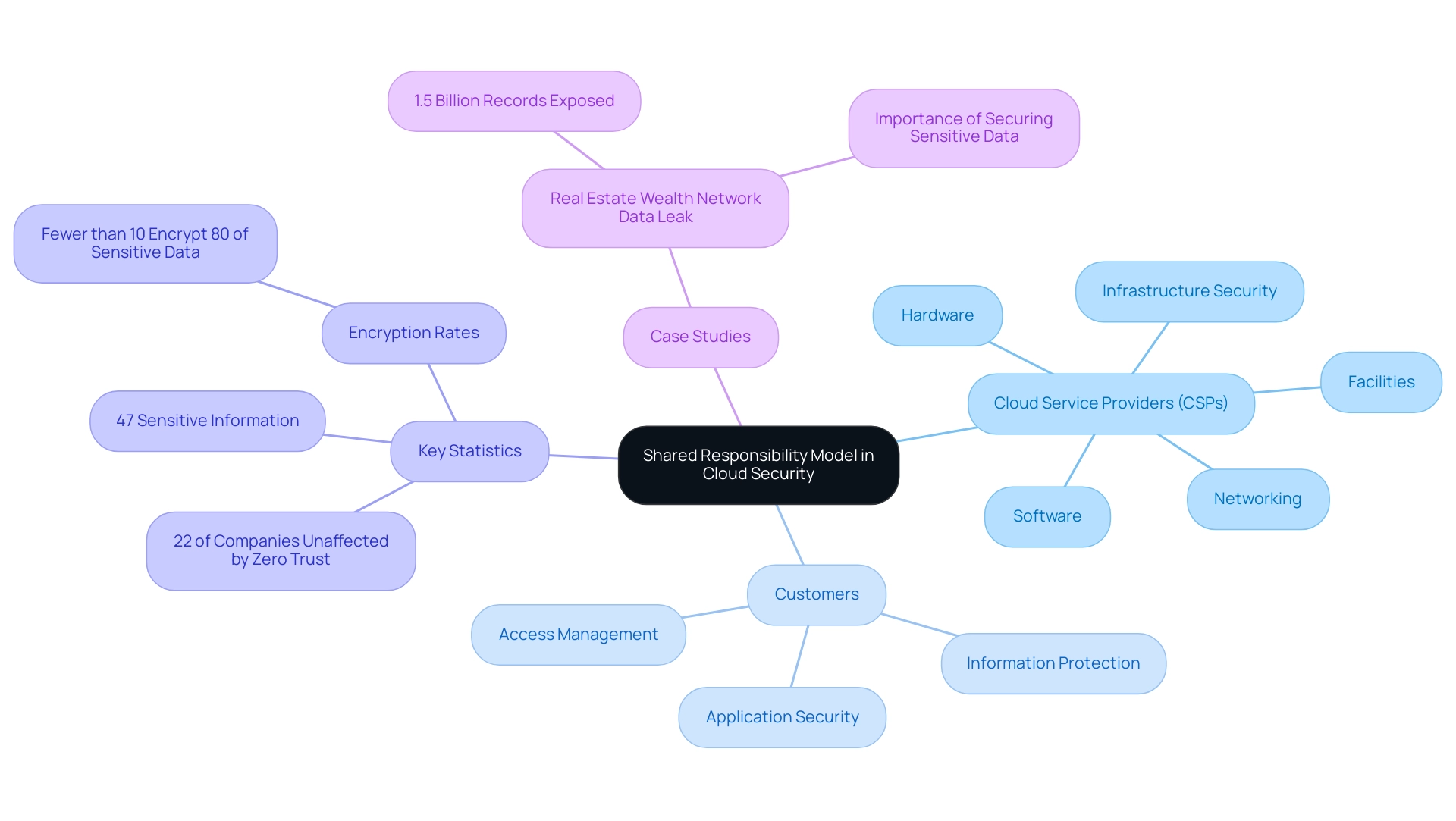
Understanding the Shared Responsibility Model in Cloud Security
The shared responsibility model in online security clearly delineates the security obligations of service providers (CSPs) versus those of their customers, emphasizing the principles of cloud security. CSPs are mainly responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, which includes hardware, software, networking, and facilities that support services. On the other hand, customers are accountable for protecting their own information, applications, and access management within the online ecosystem.
Alarmingly, a survey revealed that 22% of companies reported their online strategies remain unaffected by zero trust concepts, highlighting a critical area for improvement. Moreover, 47% of information stored online is considered sensitive, yet fewer than 10% of organizations encrypt at least 80% of their critical information, highlighting the urgency of addressing these responsibilities. Gartner has observed that 'at least 95% of cloud protection failures will be the customer’s fault,' reinforcing the critical nature of customer responsibilities in cloud protection.
The recent data breach involving the Real Estate Wealth Network, which resulted in the exposure of 1.5 billion records, starkly illustrates the dire consequences of inadequately addressing these responsibilities. To reduce such risks, entities must recognize their roles within the principles of cloud security and collaborative responsibility framework, aligning protective measures with their specific needs and regulatory requirements while promoting a proactive safety culture. Additionally, leveraging regularly updated CIS Hardened Images can enhance security measures in alignment with the shared responsibility model, demonstrating a practical approach organizations can adopt.
Conclusion
As organizations navigate the complexities of cloud security, the implementation of foundational principles and best practices is crucial for safeguarding digital assets. Central to these efforts is the CIA triad—confidentiality, integrity, and availability—which serves as the framework for effective security measures. By prioritizing data protection through robust encryption protocols, identity and access management, and a clear understanding of the shared responsibility model, organizations can significantly mitigate risks associated with cloud environments.
The importance of conducting regular security assessments, establishing comprehensive incident response plans, and investing in employee training cannot be overstated. These proactive measures not only enhance security postures but also prepare organizations to respond effectively to potential breaches. Given the alarming statistics surrounding cloud security threats, such as the high incidence of account takeovers and data breaches, adopting a multifaceted approach to security is essential.
Ultimately, organizations must recognize that cloud security is not merely a technical requirement but a strategic imperative. By embracing these best practices and fostering a culture of security awareness, organizations can protect their sensitive data and maintain operational integrity in an increasingly digital world. As the landscape of cloud technology continues to evolve, the commitment to robust security measures will be pivotal in ensuring long-term success and resilience against emerging threats.




