Introduction
As organizations navigate the complexities of modern technology, cloud computing emerges as a pivotal solution, reshaping how businesses operate and innovate. This paradigm shift encompasses three primary service models:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
Each offering unique advantages tailored to diverse business needs. With 94% of companies now embracing cloud solutions and a significant portion of their data residing in the cloud, understanding the distinctions and practical applications of these models is essential for leveraging their full potential.
This article delves into the intricacies of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, exploring their respective benefits and challenges, practical use cases, and the future landscape of cloud computing driven by emerging trends and innovations.
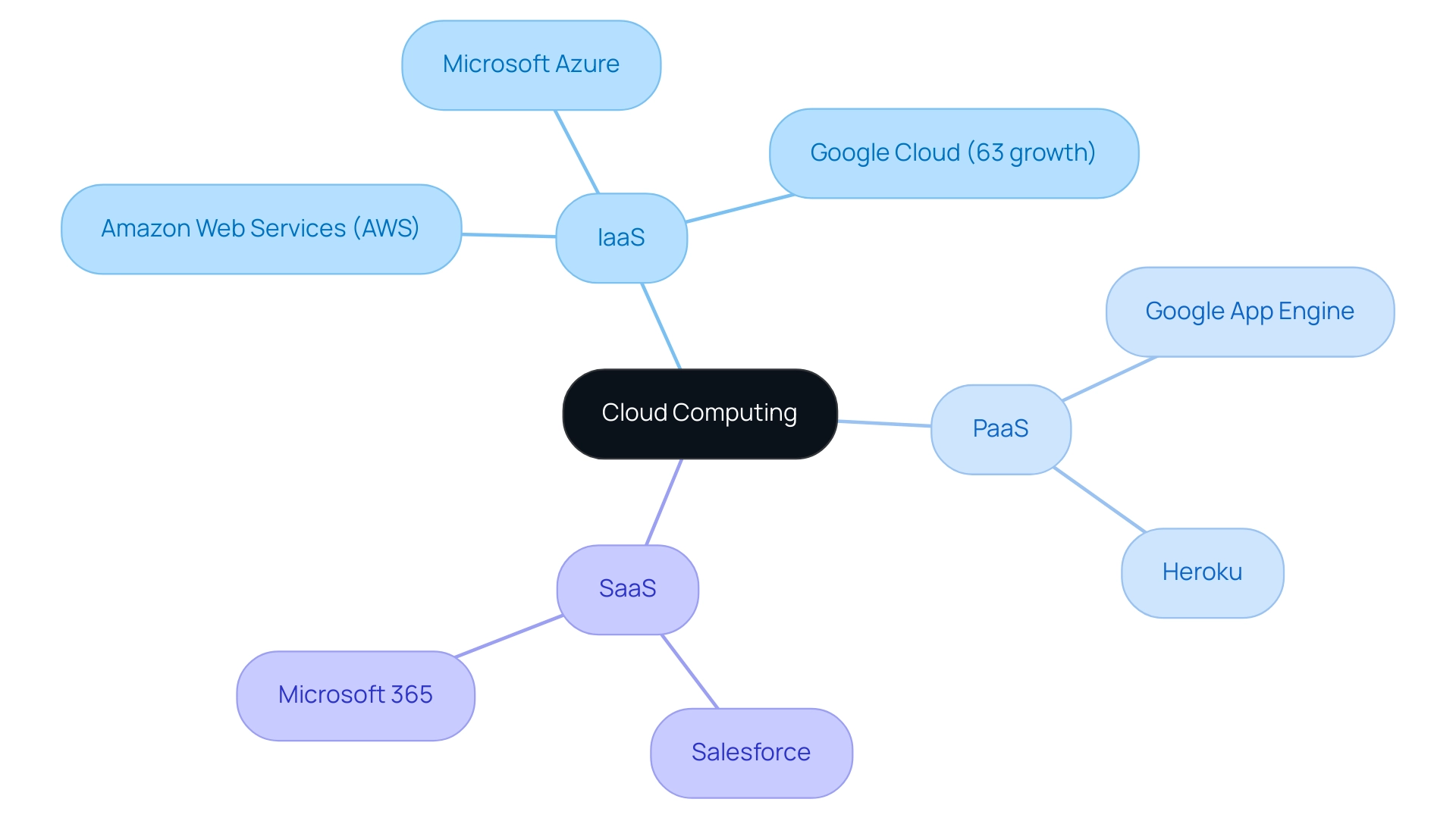
Defining Cloud Computing: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Cloud computing SaaS PaaS IaaS stands as a transformative model that delivers essential computing services over the internet, enabling organizations to leverage technology without the burdens of physical infrastructure investment. This model is categorized into three primary service frameworks: cloud computing, which includes SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. The model of Infrastructure as a Service within cloud computing SaaS PaaS IaaS offers virtualized computing resources via the internet, enabling businesses to lease servers, storage, and networking capabilities.
Noteworthy providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure. Recent analysis reveals that Google Cloud’s IaaS offering is growing at an impressive rate of 63%, according to Gartner, indicating a robust market trend towards scalable solutions.
-
Cloud computing SaaS PaaS IaaS offers a comprehensive platform that enables developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without the complexity of maintaining the underlying infrastructure.
-
Key examples include Google App Engine and Heroku, which simplify application development by providing essential tools and services.
-
The model of cloud computing SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS delivers software applications via the internet on a subscription basis, effectively eliminating the need for local installations.
-
Notable instances consist of Salesforce and Microsoft 365, which are extensively utilized for their user-friendliness and availability.
In 2023, an astonishing 94% of businesses globally are adopting cloud technology, with 60% of corporate information now stored remotely. This trend underscores the increasing trust businesses place in cloud computing SaaS PaaS IaaS solutions for data storage and management. Furthermore, 89% of entities are leveraging multi-cloud strategies, reflecting the growing demand for flexibility and resilience in their IT infrastructures.
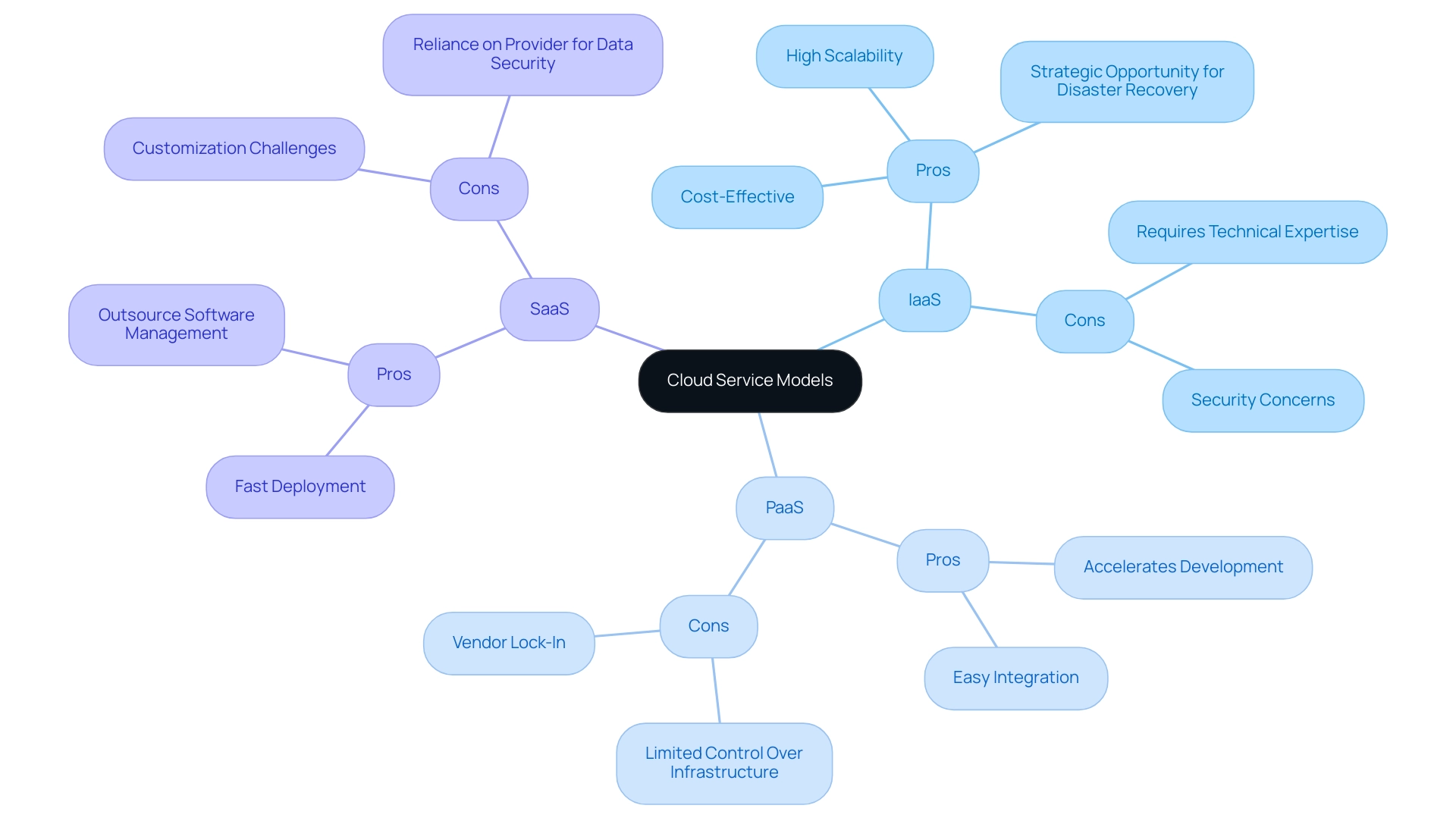
Pros and Cons of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
- IaaS:
- Pros: IaaS offers high scalability and is particularly cost-effective for organizations with variable workloads. It reduces the burden of physical hardware management, allowing businesses to focus on core operations. Considering that the infrastructure as a service market within cloud computing SaaS PaaS IaaS is projected to grow at a staggering rate of over 30%, with the U.S. and Western Europe accounting for 82% of the global cloud computing market, it presents a strategic opportunity for enterprises looking to enhance their disaster recovery solutions. Additionally, Google Cloud's infrastructure service offering is growing at an impressive rate of 63%. As Johnny Page emphasizes,
> Choosing the right one requires a full understanding of the customer needs you want to meet. -
Cons: However, effective management of IaaS necessitates a certain level of technical expertise. Additionally, organizations must be vigilant regarding potential security concerns that can arise, especially as 75% of organizations report an increase in cloud waste, highlighting the importance of efficient resource management.
-
PaaS:
- Pros: PaaS is designed to accelerate development processes, making it an appealing option for organizations with developers who possess the requisite expertise to build software fundamentals but may struggle with robust infrastructure. It facilitates easy integration with various services while significantly reducing management overhead. A notable case study titled 'When to Develop PaaS' highlights that PaaS is particularly beneficial for customers requiring app customization without the complexities of managing basic software development.
-
Cons: On the downside, PaaS users experience limited control over the underlying infrastructure, which can lead to vendor lock-in, making it crucial for businesses to evaluate their long-term commitments before adoption.
-
SaaS:
- Pros: SaaS solutions are characterized by fast deployment and automatic updates, enabling users to access applications from any location with internet connectivity. This model simplifies the IT landscape for organizations by outsourcing software management to the provider.
- Cons: Nevertheless, SaaS may present challenges in terms of customization, as users often find themselves reliant on the provider for data security and management, potentially raising concerns about data integrity and control.
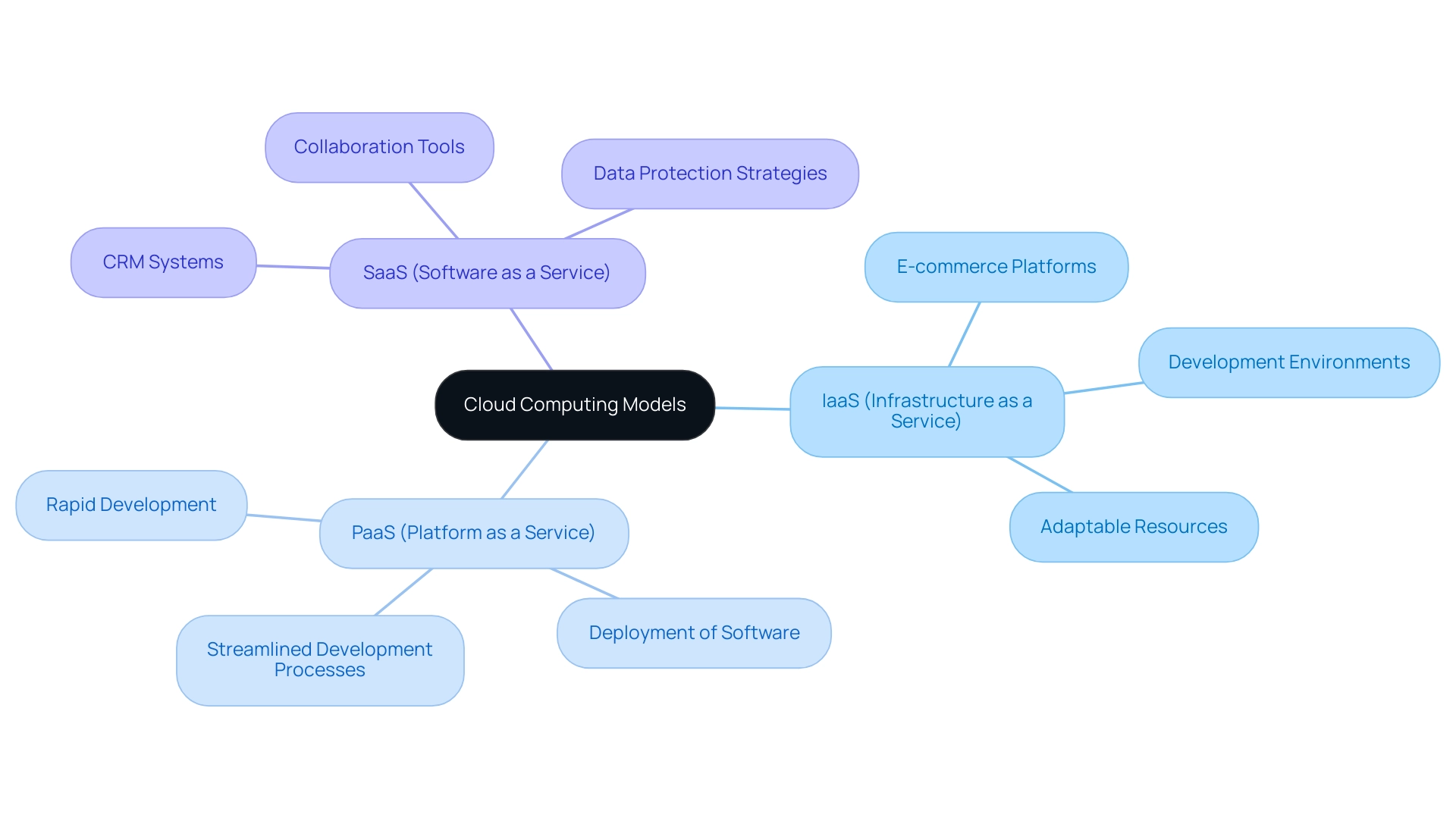
When to Use IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS: Practical Applications
-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This model within cloud computing SaaS PaaS IaaS is especially beneficial for companies that need adaptable resources to handle fluctuating workloads. For instance, e-commerce platforms often leverage cloud computing SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS during peak seasons to accommodate increased traffic and transactions, while development environments benefit from the ability to rapidly scale resources as needed. Reports suggest that as companies shift to online infrastructure, optimizing these resources is essential, particularly given the 75% of firms that have indicated a rise in digital waste, with some budgets facing waste levels as high as 47%. Effective online operating models will be essential for entities to stay competitive in a digital environment.
-
PaaS (Platform as a Service): PaaS is intended for developers seeking to leverage cloud computing SaaS PaaS IaaS to create applications without the difficulties of overseeing underlying hardware or software layers. This model is particularly beneficial for startups that are focused on rapid development and deployment of new software products. Utilizing cloud computing SaaS PaaS IaaS allows these companies to streamline their development processes, enabling them to bring innovative solutions to market more efficiently. SaaS applications, such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems and collaboration tools, provide businesses with the agility required in today's fast-paced environment. Significantly, half of surveyed companies acknowledge cloud computing SaaS PaaS IaaS as a key element of their protection strategies, further highlighting the significance of SaaS in operational resilience. Additionally, 54% of sensitive data in European companies is encrypted, highlighting the critical role of SaaS in safeguarding data. As Cody Slingerland, a FinOps certified practitioner, points out, cloud computing SaaS PaaS IaaS services facilitate efficient resource management, which is essential for modern businesses. These practical applications of cloud computing SaaS PaaS IaaS not only enhance operational efficiency but also help organizations maintain a competitive edge in a digital landscape.
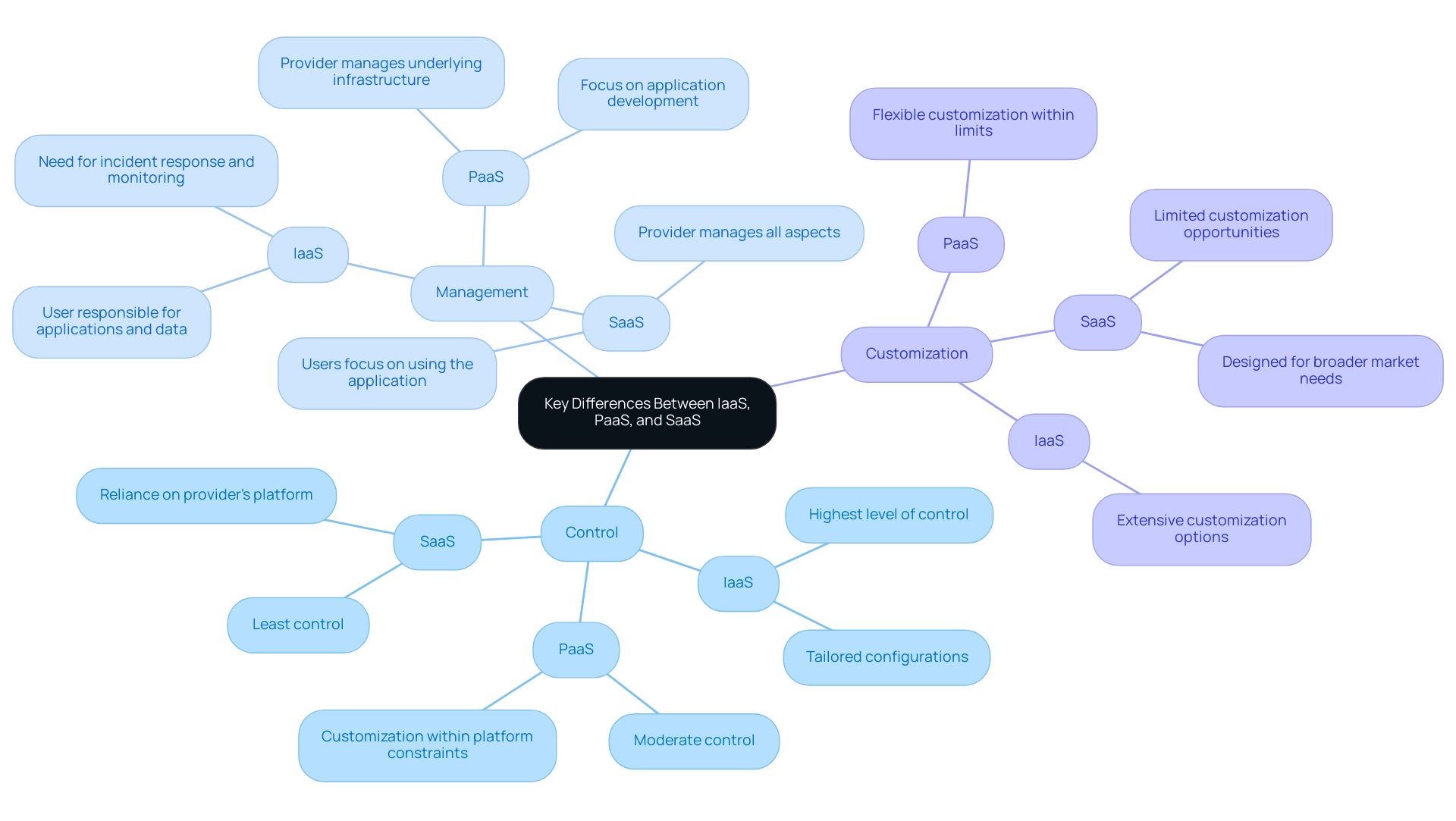
Key Differences Between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Key Differences:
-
Control: Infrastructure as a Service provides users the highest level of control over their infrastructure, allowing for tailored configurations to meet specific organizational needs. Conversely, Software as a Service (SaaS) offers the least control, as users rely entirely on the provider's platform. Multitenancy plays a crucial role here, as it enables a single software instance to serve multiple distinct user groups, enhancing operational efficiencies.
-
Management: In a cloud infrastructure model, businesses retain responsibility for managing applications, middleware, and the operating system, necessitating robust incident response and monitoring strategies. For example, a case study on infrastructure as a service emphasizes the critical need for effective monitoring and response plans to detect and address security events. In contrast, cloud computing SaaS PaaS IaaS shifts much of this responsibility to the provider, which manages the underlying infrastructure and operating system, allowing developers to focus on application development. Cloud computing SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS take this a step further, as the provider manages all aspects, from the application to the infrastructure.
-
Customization: Cloud computing SaaS PaaS IaaS facilitates extensive customization options, empowering entities to tailor their environments to specific requirements. Cloud computing SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS offers a degree of flexibility, enabling developers to customize applications within the constraints of the platform. However, cloud computing SaaS, as part of the broader cloud computing saas paas iaas model, typically presents limited customization opportunities, as solutions are designed to meet broader market needs.
As noted by OVHcloud, you can explore all of our Bare Metal, Public, and Hosted Private solutions to launch your projects, which showcases the range of options available to meet varied control and management needs in services.
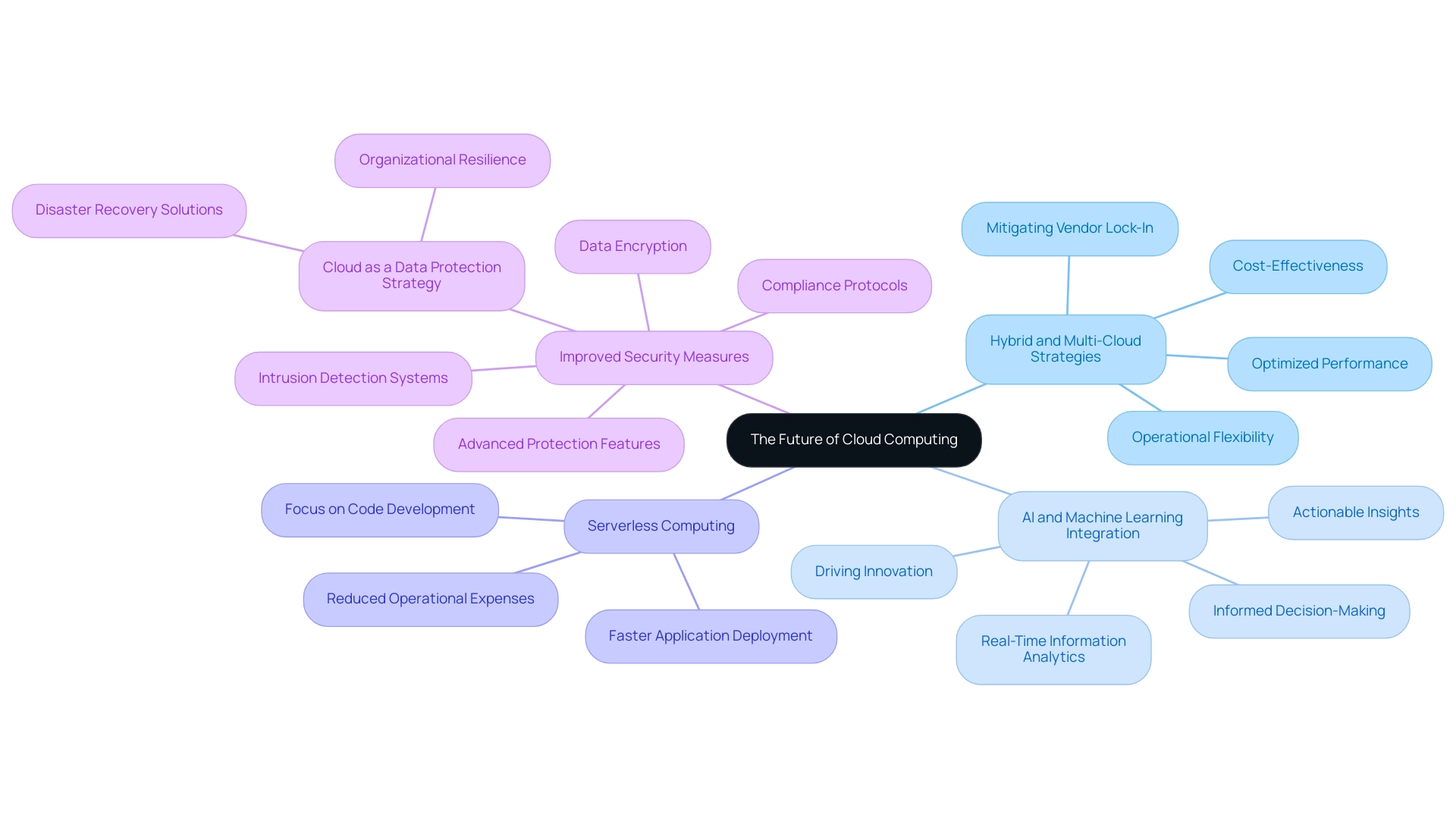
The Future of Cloud Computing: Trends and Innovations
Trends and Innovations:
-
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: An increasing number of entities are adopting hybrid and multi-cloud environments to enhance operational flexibility and mitigate the risks associated with vendor lock-in. This strategic shift enables businesses to utilize the best offerings from various providers, ensuring optimized performance and cost-effectiveness. Significantly, Google Cloud's IaaS provision within the realm of cloud computing SaaS PaaS IaaS has experienced an impressive growth of 63.7%, indicating the rising need for various online solutions.
-
AI and Machine Learning Integration: The incorporation of AI and machine learning features into online services is transforming how organizations assess and employ information. By enabling real-time information analytics, these technologies empower businesses to derive actionable insights, fostering informed decision-making and driving innovation.
-
Serverless Computing: Serverless computing is gaining traction as it allows developers to concentrate on writing code without the complexities of managing underlying infrastructure. This method not only enhances efficiency but also greatly lowers operational expenses, facilitating quicker deployment of applications.
-
Improved Security Measures: With rising worries regarding information security, service providers are prioritizing advanced protection features and compliance protocols to safeguard client information. Recent statistics indicate that half of surveyed enterprises have transitioned to online solutions for disaster recovery, underscoring the importance of these technologies in contemporary information protection strategies. As pointed out by Veeam,
The virtual environment plays a crucial role in today’s information protection strategy, according to half of the surveyed companies.
Improved security measures, including encryption and intrusion detection systems, are now standard offerings, positioning cloud computing SaaS PaaS IaaS environments as more secure than traditional IT infrastructures. Furthermore, these advanced security systems are designed to proactively address vulnerabilities that are often exploited in traditional setups, showcasing a significant upgrade in data protection.
Conclusion
Embracing cloud computing is no longer a choice but a necessity for organizations aiming to thrive in today’s digital landscape. The exploration of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) has illuminated the distinct advantages each model offers, catering to varying organizational needs.
- IaaS provides unparalleled control and scalability, making it ideal for businesses with fluctuating workloads.
- PaaS accelerates application development, allowing developers to focus on innovation without the burden of infrastructure management.
- SaaS simplifies access to essential software tools, streamlining operations and enhancing productivity.
However, with these benefits come challenges that organizations must navigate, including security concerns and potential vendor lock-in. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about their cloud strategies. As the industry trends towards hybrid and multi-cloud environments, along with the integration of AI and enhanced security measures, companies can leverage the best of cloud computing while mitigating risks.
In conclusion, the future of cloud computing is bright, driven by continuous innovations that promise to enhance operational efficiency and data security. By recognizing the unique features and applications of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, organizations can strategically align their cloud adoption with their operational goals, ensuring they remain competitive in an ever-evolving technological landscape. The path forward is clear: embracing cloud solutions is essential for fostering resilience and driving growth in the modern business environment.




