Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cloud computing, understanding the distinctions between Software as a Service (SaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS) has become essential for organizations seeking to optimize their technological infrastructure.
SaaS offers a user-friendly solution that streamlines operations by providing immediate access to software applications without the burden of installation or maintenance. In contrast, PaaS empowers developers with a flexible framework to create and manage custom applications, catering to specific business needs.
As businesses increasingly rely on cloud solutions to enhance productivity and drive innovation, grasping the nuances of these models will enable decision-makers to align their strategies with organizational goals.
This article delves into the following topics:
- Definitions
- Key differences
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Real-world applications
- Step-by-step guide for selecting the appropriate cloud model
This will equip organizations with the insights necessary to navigate the complexities of modern technology.
Understanding SaaS and PaaS: Definitions and Context
Software as a Service, commonly referred to as SaaS or PaaS, signifies a paradigm shift in software delivery, where applications are hosted in the cloud and accessible over the internet. This model eliminates the necessity for local installation and ongoing maintenance, allowing organizations to streamline operations. Notable instances include Google Workspace and Salesforce, both of which illustrate how SaaS or PaaS can enhance productivity and collaboration.
Furthermore, with 50.48% of conversions occurring through mobile devices, the accessibility of SaaS applications becomes increasingly crucial for businesses aiming to capture a wider audience. In contrast, SaaS or PaaS provides a robust framework that allows developers to create, deploy, and manage applications without the burdensome complexity of maintaining the underlying infrastructure. Notable solutions in the SaaS or PaaS category, such as Heroku and Google App Engine, empower businesses to innovate rapidly and efficiently.
Grasping these definitions is essential for CTOs, as they establish the foundation for choosing the suitable model that aligns with organizational objectives. Key features of SaaS or PaaS include:
- Scalability
- Automatic updates
- Accessibility from any device
These features make it an attractive option for many businesses. Furthermore, Goldman Sachs predicts that AI investment will near $200 billion worldwide by 2025, emphasizing the importance of online services in enabling AI progress.
As digital computing advances, it is important to recognize that the U.S. and Western Europe represent 82% of the global digital services market, indicating that these areas will continue to excel in software and platform adoption. Grasping these concepts will be essential for leveraging the full potential of technology in driving organizational success.
Key Differences Between SaaS and PaaS: A Comparative Analysis
Understanding the difference between SaaS or PaaS is essential for grasping cloud computing's varied services. The SaaS or PaaS model provides comprehensive software solutions that end-users can access directly, streamlining operations without the need for extensive technical expertise. Conversely, SaaS or PaaS offers a robust framework for developers, enabling them to build, test, and deploy applications tailored to specific business needs.
While SaaS or PaaS usually functions on a subscription model, offering predictable costs, Platform as a Service may entail fluctuating expenses depending on usage and resource consumption. This flexibility can be beneficial for organizations looking to scale their development efforts. Importantly, applications such as SaaS or PaaS are designed for immediate use, with SaaS offering a user-friendly experience, whereas PaaS requires a certain level of technical proficiency for effective implementation.
Identifying these key differences is crucial for aligning your organization's operational needs with SaaS or PaaS solutions, particularly as the demand for online services keeps increasing. Recent data indicates that by 2025, it is expected that 50% of all information will be stored online, highlighting the increasing reliance on SaaS or PaaS solutions in today's digital landscape. Moreover, half of surveyed companies have transitioned to remote storage for disaster recovery, highlighting practical reasons for embracing these services.
As Veeam observes, 'The online infrastructure plays a crucial role in today’s data protection strategy,' reinforcing the importance of such solutions in business operations. Furthermore, the digitization of life and the connectivity of smart devices lead to an exponential increase in data generation, with projections indicating that total global data will reach 200 zettabytes by 2025.
Pros and Cons of SaaS and PaaS: Weighing Your Options
Pros of SaaS:
- Ease of Use: SaaS applications are designed for user-friendliness, requiring minimal setup and allowing for quick deployment.
- Cost-Effective: With lower upfront costs, organizations can avoid the expenses associated with hardware and infrastructure, making it a financially viable option for many. Notably, 75% of organizations reported an increase in cloud waste, highlighting the importance of effective cost management in SaaS or PaaS applications.
- Automatic Updates: Software as a Service providers ensure users always have access to the latest features and security patches, eliminating the need for manual updates.
- User Satisfaction: Recent reports indicate high satisfaction rates among software as a service users, largely attributed to the ease of access and consistent performance.
Cons of SaaS:
- Limited Customization: Organizations may encounter challenges when trying to tailor SaaS solutions to their unique operational requirements, potentially limiting effectiveness.
- Dependency on Internet: Optimal performance necessitates a reliable internet connection, which can pose risks in areas with unstable connectivity.
Pros of PaaS:
- Flexibility: PaaS allows developers to build and customize applications that meet specific needs, fostering innovation and tailored solutions.
- Scalability: This model enables businesses to easily scale applications in response to fluctuating demand, without the burden of managing underlying infrastructure.
- Real-World Examples: Numerous organizations have leveraged SaaS or PaaS to accelerate development cycles, showcasing the model's capability to enhance efficiency. For instance, half of surveyed businesses view the cloud as a crucial component of their data protection strategy, using it for disaster recovery and workload migration.
Cons of PaaS:
- Complexity: Developing on a PaaS platform requires a certain level of technical knowledge, which may necessitate training and skill development for team members.
- Cost Variability: The pricing structure can fluctuate based on resource utilization, complicating budgeting and financial planning for organizations.
- Expert Opinions: Industry experts caution that while PaaS offers significant benefits, organizations must navigate its complexities to maximize value.
As online options increasingly dominate the technology landscape, understanding these advantages and disadvantages is essential for organizations aiming to enhance their digital strategies. As mentioned by UNITEDCODE, "From a professional perspective, cloud technologies will entirely supplant conventional methods, and only you can determine when to endorse this trend.
Real-World Use Cases: When to Choose SaaS or PaaS
When to Choose SaaS:
-
Small to Medium Businesses: For organizations aiming for rapid deployment and reduced IT overhead, Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions are often ideal. The attraction of software-as-a-service lies in its ability to provide immediate access to applications without the complexities of installation and maintenance. This is particularly beneficial for small to medium businesses that may not have extensive IT resources. For instance, TaskClone simplifies the process of managing tasks by integrating note-taking with task execution in apps like ClickUp, showcasing a practical application of software services in enhancing productivity.
-
Standardized Applications: Companies seeking common functionalities—such as email management, customer relationship management (CRM), or collaboration tools—find software as a service to be a resource-efficient choice. In 2024, many businesses are increasingly adopting SaaS or PaaS solutions for these standardized applications, simplifying operations while ensuring essential functionalities are readily available. This trend aligns with the broader industry movement, as evidenced by Alibaba Cloud securing a 4% market share in 2023, highlighting the competitive landscape in cloud services.
When to Choose PaaS:
-
Custom Application Development: For organizations with unique requirements necessitating tailored applications, Platform as a Service (PaaS) emerges as a compelling option. Platform as a Service not only offers the tools for custom development but also assists in integrating with existing systems, allowing developers to create solutions that align perfectly with their specific needs.
-
Rapid Development Cycles: Organizations looking to innovate quickly and implement applications effectively can utilize SaaS or PaaS for its inherent flexibility and scalability. This model is particularly advantageous in dynamic business environments where speed to market is critical. The IaaS market, which comprises elements of platform as a service, is expected to undergo significant expansion, with certain offerings such as Google Cloud's IaaS increasing at a remarkable rate of 63.7%. This trend underscores the increasing importance of PaaS in enabling organizations to stay competitive and responsive to market demands. Furthermore, it is essential to mention that based on half of the surveyed companies, "the online environment plays a vital role in today’s data protection strategy," as indicated by Veeam, further emphasizing the strategic significance of remote resources.
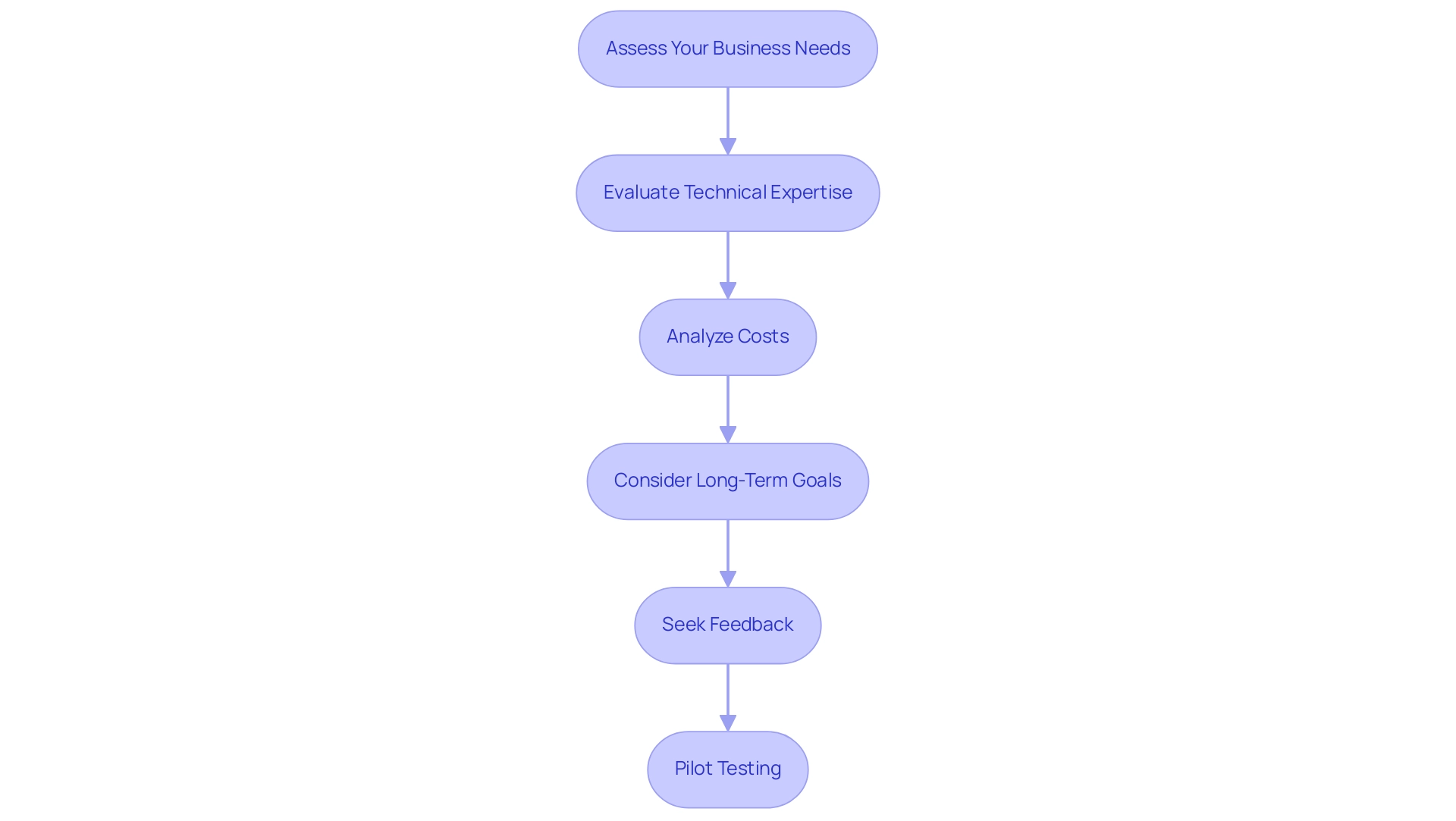
How to Choose Between SaaS and PaaS: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
Assess Your Business Needs: Begin by comprehensively identifying your organization’s specific requirements. Focus on critical aspects such as functionality, scalability, and budget constraints. Significantly, half of the businesses surveyed have moved to online services mainly for disaster recovery, highlighting the necessity of aligning these resources with your operational requirements. This trend highlights the necessity of evaluating how cloud services can enhance your business continuity strategies.
-
Evaluate Technical Expertise: Consider the capabilities of your technical team. Evaluate if your team has the essential skills to effectively support a SaaS or PaaS solution. A strong understanding of your team’s expertise can determine the feasibility of implementing a more complex platform.
-
Analyze Costs: Conduct a thorough comparison of the total cost of ownership for SaaS or PaaS models, factoring in not only upfront costs but also hidden expenses that may arise over time. Recent findings indicate that 75% of organizations are grappling with increased waste in their online storage, with some experiencing waste rates as high as 47% of their budgets. Furthermore, case studies like Drift, which lowered expenses by $2.4 million, and Obsidian, which decreased its AWS bill by 25%, demonstrate effective cost management strategies. Understanding these financial implications is crucial.
-
Consider Long-Term Goals: Ensure that your choice aligns with your organization’s strategic objectives and long-term growth plans. Prashant Acharya, Senior Communications Manager at StorX Network, notes that cloud approaches can truly make a difference in streamlining operations and enhancing security. This viewpoint emphasizes the necessity for a forward-thinking strategy when choosing digital models. Furthermore, the substantial expansion of Google Cloud's IaaS offering by 63.7% from 2020 to 2021 highlights the growing importance of cloud services in today's market.
-
Seek Feedback: Engage with stakeholders and team members to gather diverse insights and perspectives prior to making a definitive decision. This collaborative approach can unveil potential challenges or benefits that may not be immediately evident.
-
Pilot Testing: Where feasible, conduct trials of both SaaS or PaaS solutions to evaluate their compatibility with your operational environment. This hands-on experience is invaluable in assessing the practical implications of your choice.
By meticulously following these guidelines, organizations can make informed decisions that not only meet their current needs but also support their future ambitions.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between Software as a Service (SaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS) is crucial for organizations navigating the complexities of cloud computing. This article has outlined the foundational definitions, key distinctions, and the respective advantages and disadvantages of these two models.
- SaaS stands out for its ease of use and immediate accessibility, making it a preferred choice for many businesses, particularly small to medium enterprises.
- In contrast, PaaS offers a flexible environment for developers to create tailored applications, which is essential for organizations with specific needs and rapid development cycles.
The practical applications of SaaS and PaaS further illustrate their significance in today's digital landscape. As businesses increasingly leverage cloud solutions for everything from disaster recovery to application development, understanding when to deploy each model can enhance operational efficiency and drive innovation.
The step-by-step guide provided serves as a valuable resource for decision-makers, ensuring that choices align with both immediate requirements and long-term strategic goals.
Ultimately, as the reliance on cloud computing continues to grow, organizations must equip themselves with the knowledge to make informed decisions regarding SaaS and PaaS. By recognizing the unique strengths and limitations of each model, businesses can better position themselves to thrive in an ever-evolving technological environment. Embracing the right cloud solutions is not just a trend; it is a vital component of sustainable growth and competitive advantage in the modern marketplace.




