Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cloud computing, Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure have emerged as leading providers, each offering a diverse array of services designed to meet the unique needs of businesses across various sectors. As organizations increasingly seek to harness the power of cloud technology, understanding the core concepts and pricing models of these platforms becomes essential for informed decision-making.
With AWS's extensive service portfolio and Azure's seamless integration with Microsoft products, decision-makers must navigate the complexities of each platform to optimize their cloud strategies.
This article delves into the intricacies of AWS and Azure, providing a comprehensive analysis of their pricing structures, service offerings, and the implications for organizations aiming to leverage cloud solutions effectively.
As businesses transition to digital-first strategies, the insights presented here will equip them with the knowledge needed to make strategic choices that drive efficiency and innovation in their operations.
Understanding AWS and Azure: Core Concepts and Services
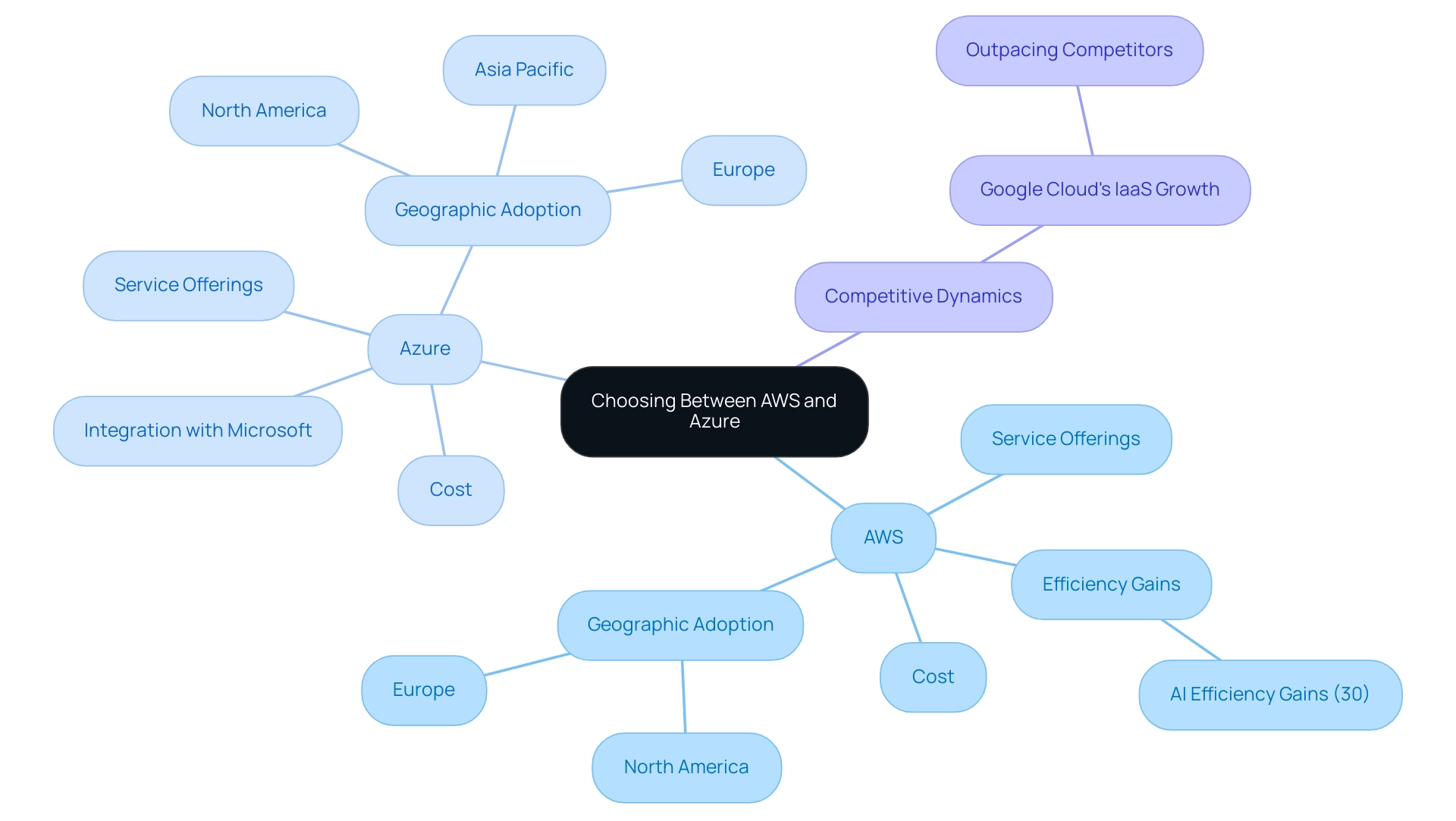
Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft stand as two of the foremost cloud service providers, each presenting a comprehensive array of services tailored to diverse business requirements. AWS, launched in 2006, has established a reputation for its robust service portfolio, which encompasses computing power, storage solutions, and networking capabilities. Its pay-as-you-go pricing model ensures that users only incur costs for the resources they actually utilize, promoting cost efficiency and flexibility.
Conversely, Microsoft’s cloud service, introduced in 2010, offers seamless integration with Microsoft products, which significantly benefits organizations already utilizing Microsoft technologies. The cloud provider's service offerings are extensive, including virtual machines, databases, advanced AI tools, and Function-as-a-Service (FAAs), allowing consumers to develop and manage application functions without maintaining infrastructure. Similar to AWS, the platform utilizes a consumption-based cost strategy.
This alignment in pricing models between AWS and Azure facilitates a straightforward comparison of cost implications, making it essential for decision-makers to grasp these foundational concepts when evaluating online solutions, particularly in the context of azure pricing vs aws. Notably, 89% of businesses report using multi-platform solutions, with 80% utilizing hybrid environments, indicating a strong trend towards diversified strategies. Furthermore, Google Cloud's revenue growth, which experienced an increase from $4.99 billion in Q3 2021 to $6.87 billion in Q3 2022, exemplifies the competitive dynamics within the services sector.
As Sid Nag, VP Analyst at Gartner, articulates,
Cloud has been elevated from a technology disruptor to a business disruptor. IaaS is propelling Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) expansion as purchasers keep integrating more applications into the online environment and upgrading current ones. This perspective underscores the significance of understanding each platform's core concepts in the context of current market trends.
Comparative Analysis of AWS and Azure Pricing Models
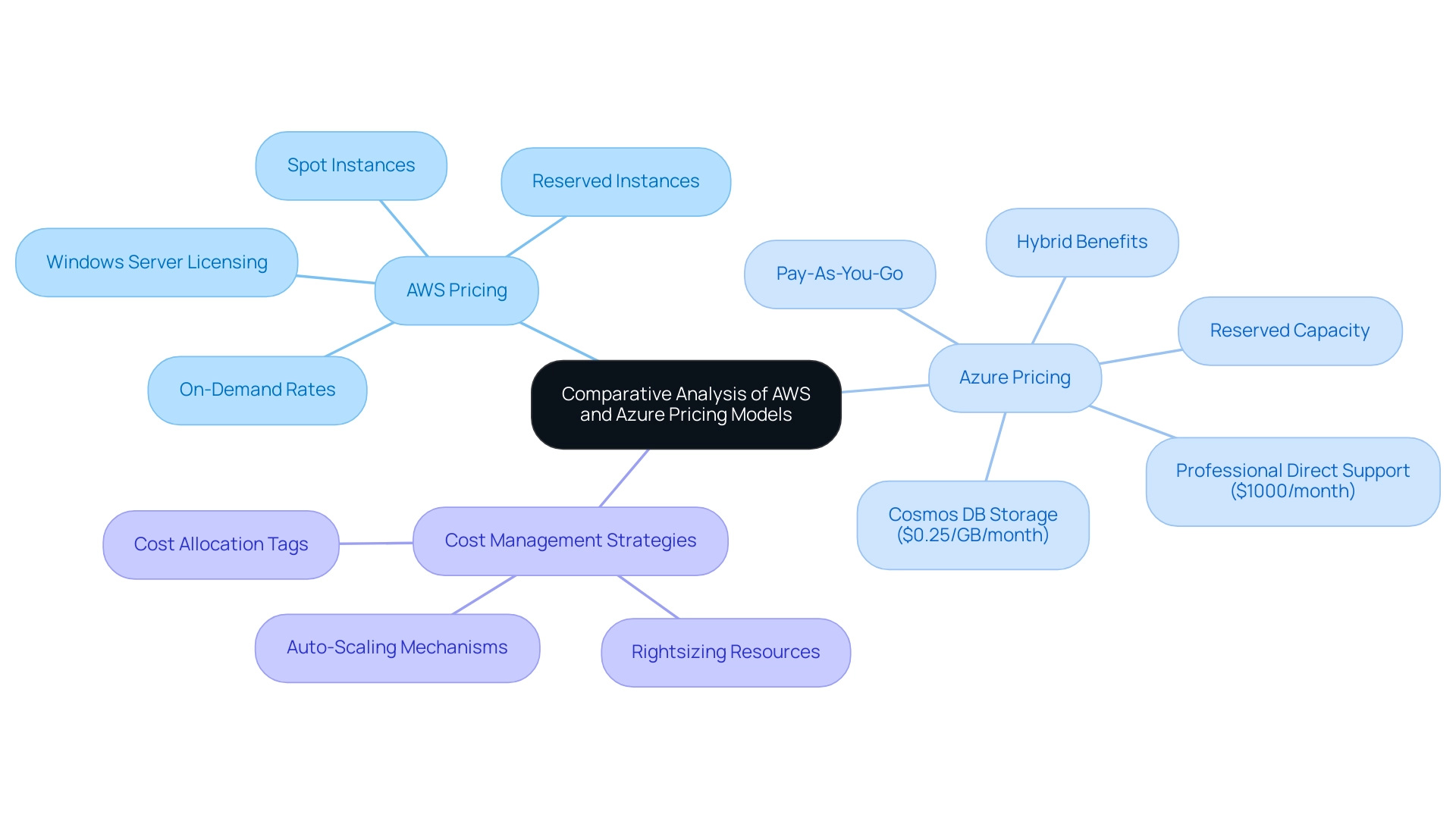
Both AWS and Azure pricing vs AWS offer a range of cost structures designed to suit various usage patterns, allowing organizations to enhance their cloud spending. AWS provides various cost options, including on-demand rates, reserved instances, and spot instances. Among these, reserved instances stand out, providing substantial savings for users willing to commit long-term.
In contrast, the platform features a pay-as-you-go pricing model, alongside reserved capacity and hybrid benefits for existing Microsoft customers, which can lead to additional savings. Notably, Cosmos DB storage is priced at $0.25 per GB per month, reflecting its competitive stance in the market. Additionally, the professional direct support costs $1000 per month, which includes high priority and quicker response times, providing users with critical support options.
Additionally, Microsoft incorporates licensing expenses into its VM costs, while AWS includes Windows Server licensing in EC2 instance rates, which is crucial for comprehending the overall cost landscape. While Azure's integration with Microsoft products can simplify costs for users already embedded in that ecosystem, when examining Azure pricing vs AWS, it is clear that AWS is often critiqued for its more intricate cost structure stemming from its vast array of service offerings. As Cody Slingerland, a FinOps certified practitioner, points out, collaborating with internal team members and subject matter experts is crucial for creating expert-written content on pricing strategies for technology.
This insight emphasizes the necessity of analyzing these models to ascertain the most financially viable option for an organization's strategy. Moreover, both AWS and Azure emphasize the importance of effective cost management strategies, as illustrated in the case study titled "Strategies to Lower Costs in Azure Pricing vs AWS," which demonstrates that users can optimize spending by:
- Rightsizing resources
- Utilizing cost allocation tags
- Implementing auto-scaling mechanisms
Understanding the nuances of these cost structures is essential for organizations aiming to navigate the complexities of cloud services successfully.
Service-Specific Pricing: Compute, Storage, and More
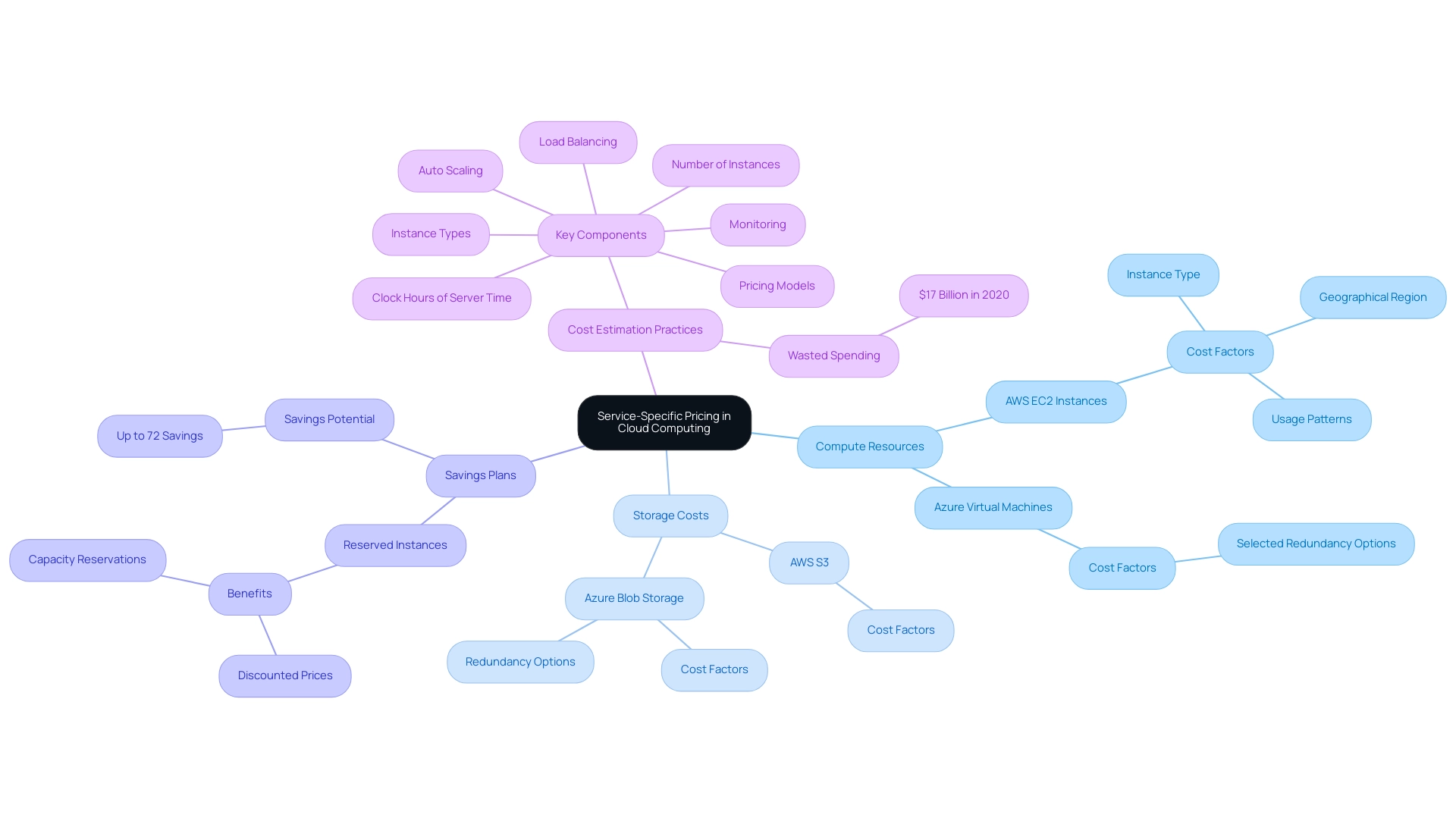
When assessing service-specific costs, compute resources such as virtual machines (VMs) emerge as a critical consideration. AWS provides EC2 instances with a range of cost options that rely on factors such as instance type, geographical region, and usage patterns. Notably, AWS's Savings Plans offer reduced rates for a commitment to a specific amount of usage over one or three years, yielding discounts of up to 72% compared to On-Demand costs.
In contrast, the platform offers a comparable array of capabilities via its Virtual Machines service, with competitive cost structures that also merit consideration. For instance, while AWS charges based on both the quantity of data stored and the number of requests made, Azure's costs operate on the basis of selected redundancy options, which can significantly affect overall expenditure. Additionally, purchasing Reserved Instances on a recurring schedule allows AWS customers to pay by the hour and obtain capacity reservations for specific time periods, offering another strategic pricing option.
Comprehending these intricacies is essential for organizations aiming to accurately predict their spending on online services. As Cody Slingerland highlighted, the staggering $17 billion in wasted spending on online services in 2020 emphasizes the need for accurate cost estimation practices. A case study on estimating Amazon EC2 costs demonstrates that key components such as clock hours of server time, instance types, and cost models are essential for effective resource allocation and expense management.
This comparative analysis of AWS S3 and Blob Storage costs further emphasizes the importance of aligning cloud expenditures with operational requirements, providing a comprehensive view of both AWS and the other platform's cost strategies.
Pros and Cons of AWS vs. Azure: Cost-Effectiveness and Value
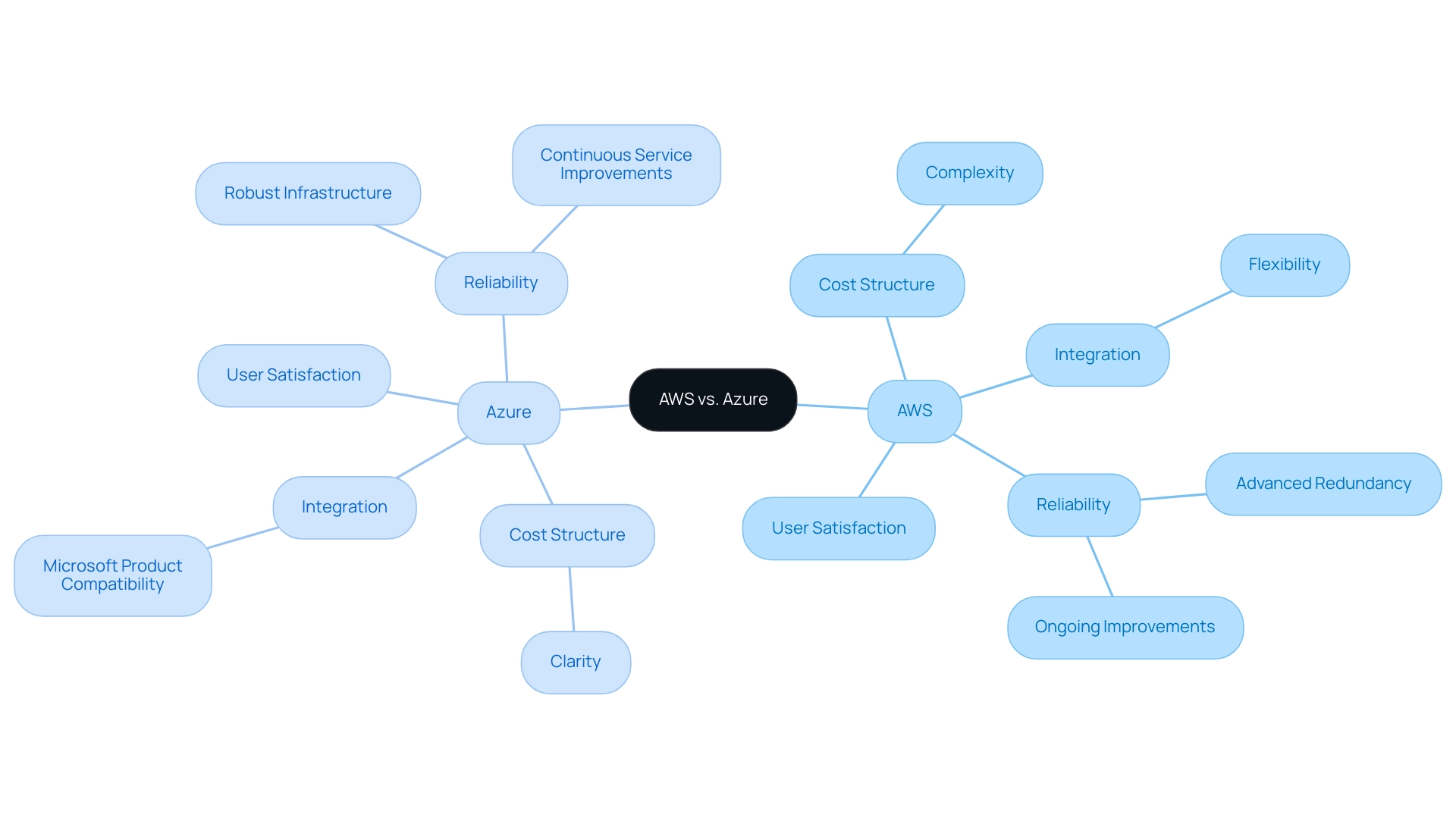
AWS is frequently recognized for its extensive range of services and inherent flexibility, which can translate into significant cost savings for organizations capable of effectively managing their resources. However, the complexity of its cost structure remains a notable challenge for users seeking clear and straightforward cost estimates in the context of azure pricing vs aws. In contrast, this platform stands out because of its smooth integration with Microsoft products and its clearer cost structure, making it an ideal solution for businesses already using tools like Office 365 or Dynamics, particularly when evaluating azure pricing vs aws.
While the cloud service may offer a more favorable pricing model for Windows-based workloads, analyzing azure pricing vs aws shows it does not always compete in terms of feature depth and breadth. According to recent findings, half of surveyed organizations have migrated to remote servers primarily for disaster recovery, underscoring the importance of robust and reliable solutions. Both platforms boast strong reliability, characterized by advanced redundancy and ongoing improvements, which are critical for modern data protection strategies.
Significantly, numerous organizations have effectively lowered their expenses on computing services through strategies emphasized in the 'Cost Management Success Stories,' showcasing efficient methods for handling costs while utilizing both AWS and other platforms. Ultimately, the choice between AWS and other cloud platforms should be guided by an organization’s specific requirements, current technology stack, budgetary constraints, and considerations such as azure pricing vs aws. This strategic decision can significantly impact cost-effectiveness, user satisfaction, and overall operational efficiency in the evolving landscape of computing.
Key Takeaways: Choosing Between AWS and Azure Based on Costs
Both AWS and other platforms offer strong online services with distinct pricing strategies, especially when comparing Azure pricing vs AWS, designed for various business needs. As organizations contemplate their strategies for 2024, it is essential to evaluate particular operational requirements, current technology investments, and expected growth trajectories. Transitioning to an AI-intrinsic business model necessitates fundamental changes across the value chain, which, while time-consuming, offers clear rewards.
Recent insights indicate that efficiency gains in software development attributed to AI reach upwards of 30%, underscoring the importance of selecting a platform that aligns with an organization’s digital transformation goals. AWS is often favored for its extensive service offerings and flexibility, making it an appealing choice for businesses requiring a wide array of functionalities. Conversely, Azure may offer superior value for organizations deeply integrated into the Microsoft ecosystem, leveraging existing tools and expertise.
Charles Griffiths, Director of Technology and Innovation, emphasizes that
Cloud computing has transformed both the business world and our personal lives.
This transformation emphasizes the necessity for informed decision-making, where an understanding of Azure pricing vs AWS and services directs organizations toward successful digital strategies. As cloud adoption accelerates in North America and Europe—regions currently leading the way, with Asia Pacific rapidly closing the gap—businesses must remain vigilant in evaluating their options to achieve a competitive edge.
Notably, Google Cloud's IaaS growth has outpaced competitors in certain areas, exemplifying the competitive dynamics that organizations must consider when choosing between AWS and Azure.
Conclusion
In the competitive realm of cloud computing, Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure stand out as premier providers, each offering distinct advantages and pricing models that cater to varying business needs.
- AWS is recognized for its extensive service offerings and flexibility, while
- Azure excels in its integration with Microsoft products, providing a streamlined experience for organizations already embedded in that ecosystem.
Understanding these foundational elements is crucial for decision-makers as they navigate their cloud strategies.
The comparative analysis of pricing models reveals the importance of tailoring cloud expenditures to specific operational requirements. Both AWS and Azure utilize consumption-based pricing, yet their structures differ significantly, necessitating a careful examination to optimize costs. Organizations must leverage strategies such as reserved instances and effective cost management practices to ensure that they maximize the value derived from their cloud investments.
Ultimately, the decision between AWS and Azure should be informed by a comprehensive assessment of an organization’s unique requirements, existing technology stack, and long-term growth objectives. As businesses increasingly adopt digital-first strategies, the insights provided in this analysis will empower them to make strategic choices that not only enhance operational efficiency but also drive innovation in an ever-evolving technological landscape.
In this context, informed decision-making is paramount, ensuring that organizations harness the full potential of cloud solutions to achieve a competitive advantage.




