Introduction
Navigating the complex landscape of cloud computing pricing can be a daunting task for organizations striving to optimize their budgets while harnessing the full potential of cloud services. With major players like Azure and AWS offering distinct pricing models, understanding the nuances of each platform is essential for making informed decisions that align with financial goals. From the flexibility of AWS's pay-as-you-go structure to Azure's subscription-based options, companies must carefully evaluate their usage patterns to avoid unexpected costs.
As businesses increasingly rely on cloud solutions, the importance of effective cost management strategies becomes paramount. This article delves into the intricacies of Azure and AWS pricing models, explores key cost factors across compute, storage, and database services, and highlights optimization strategies that can lead to significant savings. By examining case studies and expert insights, organizations can better navigate their cloud journey and enhance their financial performance in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Comparative Overview of Azure and AWS Pricing Models
The cloud platforms have different pricing models, which can be analyzed through Azure cost vs AWS, tailored to meet diverse business requirements. AWS functions mainly on a pay-as-you-go model, where expenses are generated based on actual resource usage, including fees for data transfers out of its regions. While this model offers flexibility, it can lead to unpredictable expenses if usage is not carefully monitored.
On the other hand, Azure presents a similar pay-per-use pricing approach but enhances predictability through subscription-based options, facilitating more straightforward budgeting processes and providing free inbound data transfers. Both platforms provide pricing calculators intended to assess expenses based on anticipated usage, yet the complexity of their pricing frameworks can often be daunting for users. Tools created by both AWS and Microsoft, such as CloudZero, allow organizations to establish budgets and receive alerts on spending anomalies, thereby assisting in effective financial management and optimization.
As Nanda Kishore, a technical writer, notes, 'His clear explanations on technological topics help readers to navigate through the industry.' Comprehending these pricing models, including the Azure cost vs AWS, is essential for businesses seeking to align their strategies with financial objectives, particularly in light of the recent updates on pricing strategies for 2024. A case study titled 'Tools and Services for Cost Management and Optimization' illustrates how various tools developed by AWS and Microsoft assist organizations in managing costs and optimizing pricing for online services, facilitating budget management and pricing calculations.
Key Cost Factors: Compute, Storage, and Database Pricing
In the realm of cloud computing, the comparison of azure cost vs aws reveals that compute pricing varies considerably between the two platforms, each offering a diverse array of instance types that cater to different performance needs. While AWS excels with its extensive range of instance offerings, a comparable platform provides flexible options, which brings up the discussion of azure cost vs aws at different price points. A critical aspect of expense analysis lies in storage charges.
- The Blob Storage service often appears as a more economical option for managing large datasets compared to AWS S3, dependent on specific usage patterns.
- Furthermore, the pricing structures for database services on these platforms exhibit notable distinctions.
- The SQL Database generally employs a pricing model based on Database Transaction Units (DTUs),
- while AWS RDS uses a pricing structure dependent on instance size and allocated storage.
Such variations highlight the significance of a comprehensive assessment of organizational workloads and use cases, as the evaluation of azure cost vs aws could lead to substantial financial implications. According to CloudZero, brands have the potential to save up to $4 million by optimizing their expenses, emphasizing the need for detailed expenditure analysis. Furthermore, Azure provides different support levels, such as basic, developer, standard, and professional direct assistance, with fees varying from $29 to $1000 per month, which can affect overall pricing choices.
As highlighted in a recent case study on Compute Optimized Instance Discounts, AWS’s c6a. Xlarge is priced at $0.1010 with a 38% discount, while Google Cloud's c2-standard-4 boasts the highest discount at 41% but is still not the cheapest. As Laurent Gil aptly noted,
Compute often results in accumulating a bill, but it also offers the greatest opportunity for expense optimization.
Hence, organizations must engage in detailed cost analysis to effectively leverage these cloud services.
Performance vs. Cost: SQL Server Workloads on Azure and AWS
When deploying SQL Server workloads, the platform generally excels in integration and performance optimization, owing to its native support for Microsoft technologies, including features such as geo-replication that enables seamless database replication across regions. This capability enhances data availability and resilience, aligning well with organizations that prioritize Microsoft solutions. Furthermore, a hybrid approach combining services from both Microsoft Cloud and AWS can deliver optimal results for SQL Server deployments, allowing organizations to leverage the strengths of each platform based on their unique requirements.
Conversely, AWS provides a compelling advantage in terms of pricing flexibility, particularly with its reserved instances. Organizations utilizing these options may uncover substantial savings, as AWS incorporates Windows Server licensing in its EC2 instance pricing with Bring Your Own License (BYOL) opportunities. The decision regarding Microsoft’s cloud platform versus AWS for SQL Server workloads is ultimately influenced by specific performance requirements and the azure cost vs aws.
It is vital for organizations to perform a comprehensive assessment of the overall expense of ownership, particularly when evaluating azure cost vs aws in relation to the expected performance results.
As emphasized in the case study titled 'Choosing Between AWS and Another Service for SQL Server,' organizations should align their service selections with existing infrastructure, SQL Server version needs, and integration capabilities to foster future growth. This is further emphasized by Sachin Vinay, a Network Administrator, who notes,
Our organization is safer because each Microsoft solution offers a different layer of security, and the solutions work together natively to deliver coordinated detection and response across our environment.
This underscores the necessity of considering both security and integration when selecting a cloud service for SQL Server workloads.
Cost Optimization Strategies for Azure and AWS Users
To efficiently enhance expenses on AWS, organizations should utilize auto-scaling features that dynamically modify resource allocation in response to changing demand. This proactive approach mitigates the risks of over-provisioning, which can lead to unnecessary expenses. Both Microsoft Cloud and AWS provide different pricing models, including reserved instances and savings plans, that can lead to significant reductions when evaluating Azure cost vs AWS for workloads with predictable usage patterns.
Significantly, Azure's Hybrid Benefit enables users to utilize existing on-premises Windows and SQL Server licenses for substantial discounts on Azure VMs, further improving optimization strategies. Furthermore, a regular examination of usage reports is vital; utilizing management tools like CloudZero allows users to monitor spending trends and pinpoint underutilized resources that could be suitable for reduction or removal. CloudZero plays an essential part in enhancing expenses by offering insights into spending patterns across various service providers.
Furthermore, adopting hybrid computing strategies can provide the flexibility to balance performance needs with cost savings, allowing organizations to leverage the strengths of both platforms. As demonstrated in the case study titled 'Incremental Optimization with Cloud-Native Design,' organizations often transition to remote services using a lift-and-shift approach, which can carry over inefficiencies from on-premises systems. By implementing gradual design modifications to legacy applications, organizations can eliminate inefficiencies and reduce waste over time.
As Julia Arpag, CEO & Founder of Aligned Recruitment, notes,
Great insights on online pricing strategies! It's certainly a balancing act between flexibility and savings. Adopting these strategies not only promotes resource optimization but also improves the overall efficiency of cloud operations.
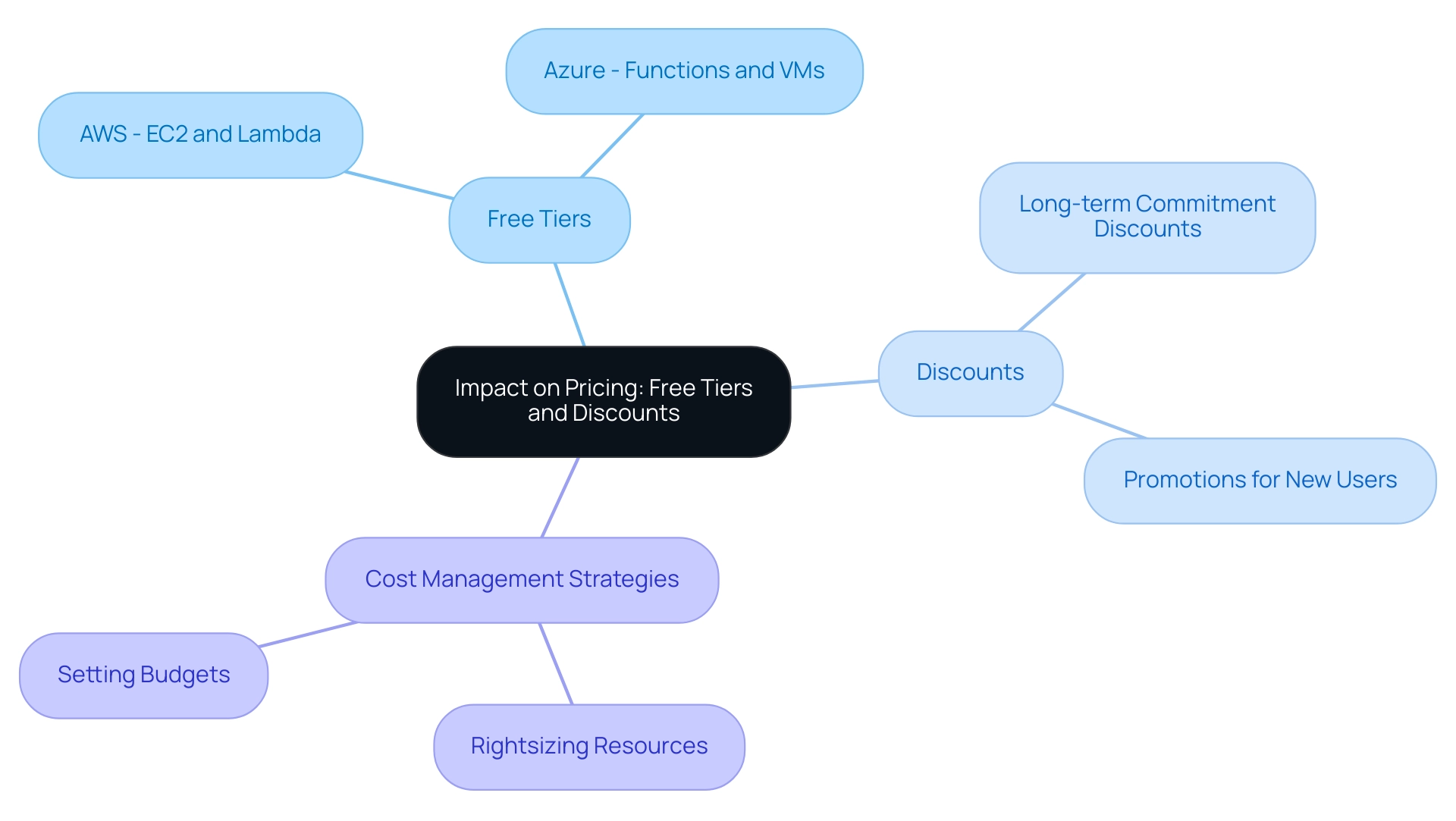
Exploring Free Tiers and Discounts: Impact on Pricing
Both AWS and another provider offer free tiers aimed at giving users restricted access to their services without incurring expenses for a designated time period. The free tier from Microsoft features offerings such as Functions and select virtual machines, while AWS mirrors this with services including EC2 and Lambda, available for the first year of use. These free tiers not only facilitate an initial exploration of online capabilities but also play a crucial role in lowering entry barriers for businesses embarking on their digital journey.
Furthermore, both platforms regularly introduce discounts for long-term commitments and special promotions aimed at new users. Such initiatives are vital as they significantly enhance accessibility and affordability for organizations. However, it is imperative for users to scrutinize the terms associated with these free tiers to prevent unexpected charges once the promotional period concludes.
For instance, Automation has a job runtime limit of 500 minutes, which users should factor in when planning their usage. Additionally, it is important to note that the big three service providers collectively control about two-thirds of the global market, highlighting the competitive landscape in which Azure and AWS operate. As noted by Meghan Neville, Content Marketing Coordinator,
Whether you seek scalability, seamless integration, or cutting-edge innovation, we'll assist you in identifying which major provider aligns best with your business goals.
This understanding emphasizes the significance of making informed decisions to enhance service utilization and manage expenses efficiently. Moreover, companies are adopting strategies to control expenses efficiently, including rightsizing resources and setting budgets, as demonstrated in the case study on managing online service expenditure, particularly when considering azure cost vs aws. These effective cost management strategies are essential for businesses to optimize their cloud spending.
Conclusion
Understanding the pricing models of Azure and AWS is crucial for organizations looking to optimize their cloud expenditures while maximizing service benefits. This article has highlighted the fundamental differences between the two platforms, from AWS's flexible pay-as-you-go structure to Azure's subscription-based options, emphasizing the need for businesses to assess their unique usage patterns. The intricacies of compute, storage, and database pricing further illustrate the importance of a tailored approach to cost management, revealing that even minor adjustments can lead to substantial savings.
Moreover, the evaluation of SQL Server workloads demonstrates that choosing the right cloud service extends beyond mere cost considerations and into the realm of performance and integration capabilities. Organizations must carefully weigh their current infrastructure against the features each platform offers, ensuring that their decisions align with both immediate needs and long-term growth strategies.
Implementing effective cost optimization strategies, such as:
- auto-scaling
- leveraging free tiers
can significantly enhance cloud efficiency and reduce unnecessary expenses. By adopting a proactive approach to cloud management, organizations can not only navigate the complexities of pricing models but also create a sustainable framework for ongoing cost control. In an increasingly competitive cloud landscape, the ability to make informed, strategic decisions will be paramount for achieving financial goals and operational excellence.




